MFT Gateway is a hosted Software as a Service (SaaS) solution that enables file exchange over the AS2 or SFTP protocol, without the need to install or maintain.
- Blog
- Is FTPS Faster Than SFTP? Speed vs Security Explained
SFTP
Is FTPS Faster Than SFTP? Speed vs Security Explained
SFTP is more secure and easier to manage than FTPS, with fewer ports, lower risks, and simpler firewall configuration for secure file transfers

Samadhi Kariyawasam
Published: 01 Aug 2025

Table of Contents
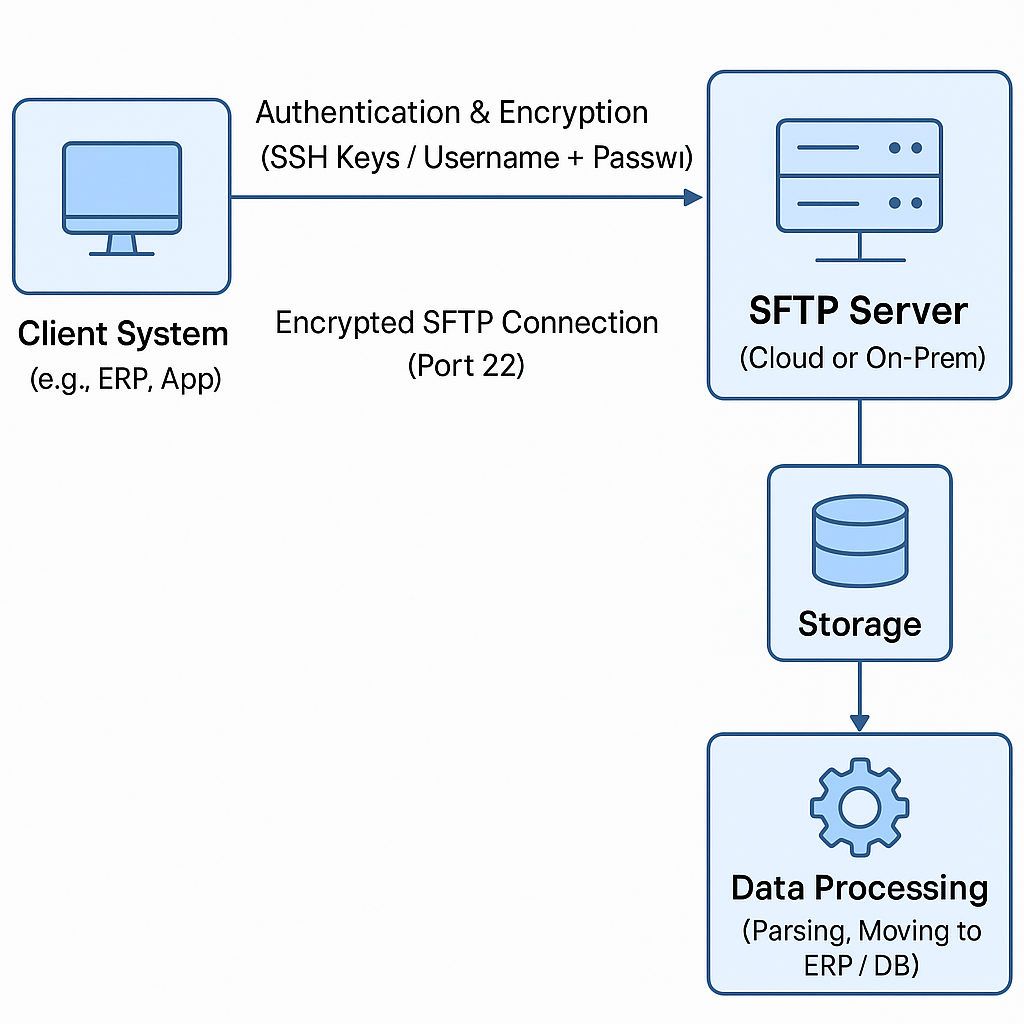
What is SFTP?
SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol or Secure File Transfer Protocol) is a widely used secure file transfer protocol. It uses the SSH (Secure Shell) protocol to provide a secure channel for transferring files across a network, typically between a partner system and yours. Unlike FTP, which sends data in plain text and frequently uses multiple ports, SFTP is entirely based on a single, encrypted SSH connection—typically port 22. This implies that all commands, file contents, and credentials are encrypted, providing robust security against eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. SFTP supports a variety of file operations, including uploading, downloading, renaming, deleting, and changing file permissions, making it not only a safer alternative to FTP but also more robust and firewall-friendly.
What is FTPS?
FTPS (FTP over SSL/TLS) is an extension of the standard File Transfer Protocol (FTP) that supports cryptographic security via SSL or TLS. It facilitates secure file transfers by encrypting both the command and data channels, preventing sensitive information like usernames, passwords, and file contents from being intercepted during transit. FTPS has two modes: explicit FTPS, where the client requests security upgrades on the standard FTP port (21), and implicit FTPS, where security is enforced from the start of the connection, usually on port 990. While FTPS provides secure encryption and integrates with existing FTP infrastructure, it can be difficult to configure because it uses numerous ports for data transfer. FTPS is also widely utilized on occasions where compliance with security regulations (such as HIPAA and PCI-DSS) must be followed.
FTPS vs SFTP
Secure Shell File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) and File Transfer Protocol Secure (FTPS) are both used for secure file transfers, but they differ significantly in architecture, compatibility, and usage. SFTP is built on the SSH (Secure Shell) protocol, extending it with file transfer capabilities, while FTPS enhances the traditional FTP protocol with SSL/TLS encryption. SFTP operates through a single port, which simplifies firewall configurations, whereas FTPS requires multiple ports—including a secondary data connection—making it more complex to configure with firewalls.
When it comes to performance, SFTP has higher overhead due to encryption, which can slow down transfers slightly, while FTPS tends to be leaner and faster. SFTP supports only binary transmission, limiting user control over file modes, whereas FTPS supports both binary and ASCII modes, making it easier to manage file types and logs.
Authentication is also handled differently in the two protocols. SFTP relies on out-of-band authentication, often using public/private key pairs without needing signed certificates, while FTPS mandates a public-key certificate for the server to authenticate securely. Additionally, SFTP provides granular command support, including fine control over file permissions and directory operations, whereas FTPS offers a more limited set of commands. Finally, in terms of adoption, SFTP has become the preferred standard and is widely supported by modern servers and cloud services, while FTPS, built on the older FTP standard, is gradually being replaced by more modern protocols like HTTPS.
Which is faster: FTPS or SFTP?
Between the two protocols, FTPS is generally considered faster in terms of transfer speed. This is primarily because SFTP transmits control, synchronization, and data packets over a single channel, which can introduce slight delays due to serialized communication. In contrast, FTPS was designed for higher performance, using separate connections for control and data channels that operate asynchronously, enabling more efficient and faster data transfers. Consequently, SFTP might be slightly slower than FTPS; however, this difference is usually not substantial in most scenarios.
Conclusion
While FTPS may offer slightly faster transfer speeds than SFTP, speed alone should not be the deciding factor when choosing between the two. SFTP provides several critical advantages that often outweigh the minor performance difference. One of the most significant benefits is its simplicity and lower administrative overhead. Because SFTP operates over a single port (typically port 22), it’s much easier to configure and secure—especially in environments with strict firewall rules. In contrast, FTPS requires multiple ports for control and data channels, complicating firewall configurations and increasing the number of potential attack vectors. With fewer ports to manage, SFTP reduces complexity, minimizes security risks, and simplifies ongoing maintenance, making it a more efficient and secure choice for many organizations.

Talk to an EDI Expert
Join hundreds of organizations already taking full control of their B2B AS2 communications with our trusted solutions. Contact us today to tailor a solution that fits your specific AS2 EDI needs.
Related Articles
View All BlogsExplore our product stack
Try before you buy with a 30-day Free Trial
No commitment, all value. Try the AS2 Solution Risk-Free and discover how our solutions can transform your business workflows. No credit card required.
Explore Your Possibilities
Elevate AS2 Communications with our EDI and AS2 Solutions
See how our AS2 and EDI solutions can simplify your integrations, boost efficiency, and keep you compliant—request a personalized demo today.