MFT Gateway is a hosted Software as a Service (SaaS) solution that enables file exchange over the AS2 or SFTP protocol, without the need to install or maintain.
- Blog
- What is an AS2 Message Disposition Notification?
AS2
What is an AS2 Message Disposition Notification?
Learn about AS2 MDNs, digital signatures, and the differences between sync and async MDNs for secure file transfers.

Dinuka Ekanayake
Published: 17 Jan 2025

AS2 is a widely-used protocol that enables secure and standardized communication of messages, including EDI messages, over the internet using the HTTP or HTTPS protocols as the transport mechanism. AS2 ensures data integrity and confidentiality during transmission by providing encryption, digital signatures, and acknowledgments.
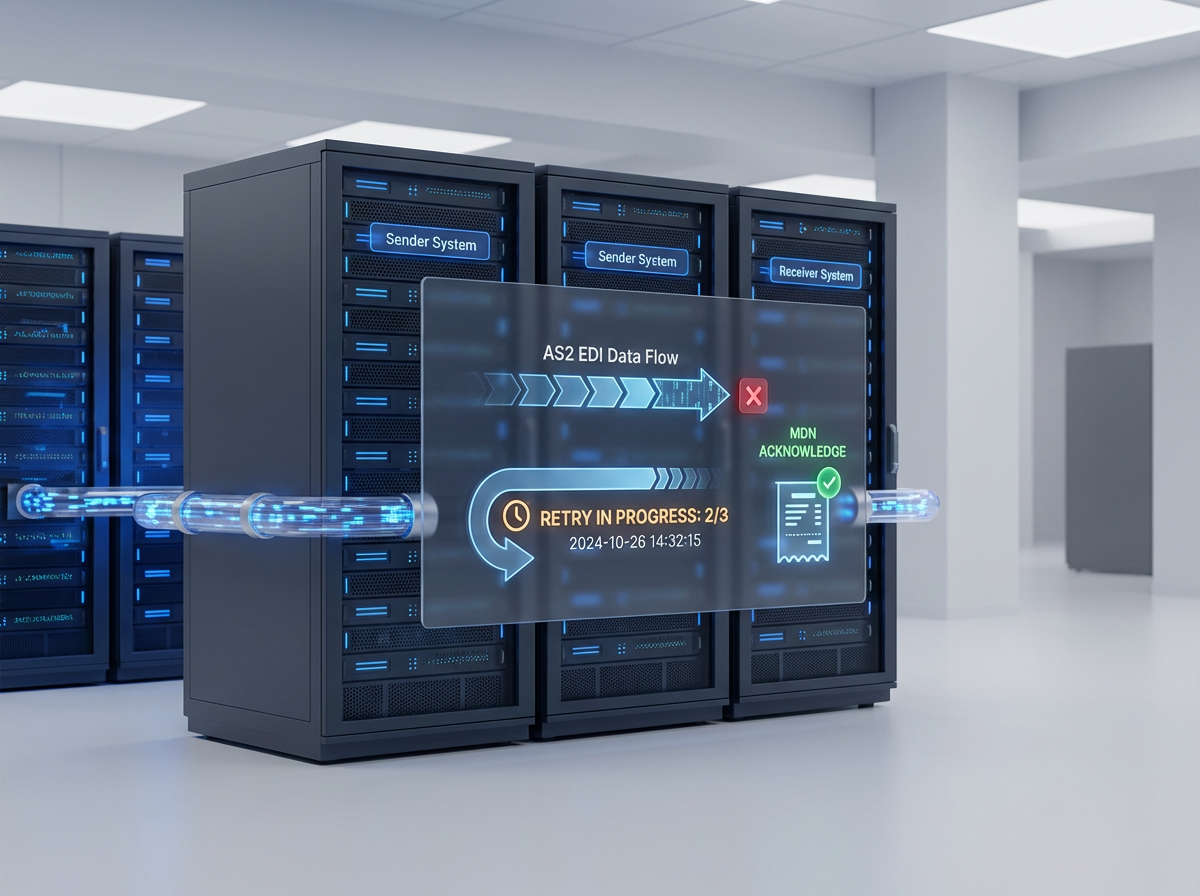
A key feature of AS2 is the use of Message Disposition Notifications (MDNs), which provide senders with verifiable confirmation that their messages have been successfully received and processed without any issues.
What is an MDN, and Why is it Needed?
An MDN (Message Disposition Notification) is a digital acknowledgment that confirms the successful receipt of an AS2 message by the recipient. It serves as a digital receipt, informing the sender that the message was delivered to the intended recipient without any issues.
MDNs are essential for several reasons including,
-
Verification of Message Successful Delivery: Without an MDN, the sender has no way of verifying whether the message was successfully received. The MDN provides confirmation that the recipient’s AS2 system has received the message without any issues.
-
Confirmation of Message Integrity: During AS2 communication, messages are encrypted and signed to protect the content. An MDN includes a status that indicates whether the decryption and signature verification processes were successful, confirming that the message was received unchanged.
-
Non-repudiation in AS2: Another key advantage of the AS2 protocol is it allows for non-repudiation, enabling the sender to confirm that the file was received and acknowledged by the receiver in an uncompromised and intact state.
Digital Signatures in MDNs
In AS2 communication, security and trust are critical factors. A digital signature in an MDN is a cryptographic mechanism that binds the sender’s identity (the recipient of the AS2 message) to the transmitted data (the MDN). This ensures authenticity, confirming that the MDN received from the intended recipient, and allows non-repudiation.
The Process of Digital Signatures in MDNs
Before exchanging messages over AS2, both parties share their public keys. Each public key matches a private key, which is used by its owner to create a digital signature. The private key is kept secret and never shared, while the public key is used to verify digital signatures. A signature can only be validated by the public key that matches its corresponding private key.
-
Requesting a Digitally Signed MDN: When sending an AS2 message, the sender requests a digitally signed MDN in the AS2 message headers, ensuring the acknowledgment includes a digital signature for more security.
-
Signing the MDN: After successfully receiving and processing the AS2 message, the recipient generates an MDN and uses their private key to add a digital signature. This signature serves as a unique fingerprint, linking the MDN to the recipient.
-
Verifying the MDN’s Authenticity: When the sender receives the digitally signed MDN, they verify its authenticity using the recipient’s public key. Once the signature has been validated, the sender knows the MDN is from the right trading partner and the AS2 transmission was successful.
Synchronous vs. Asynchronous MDNs
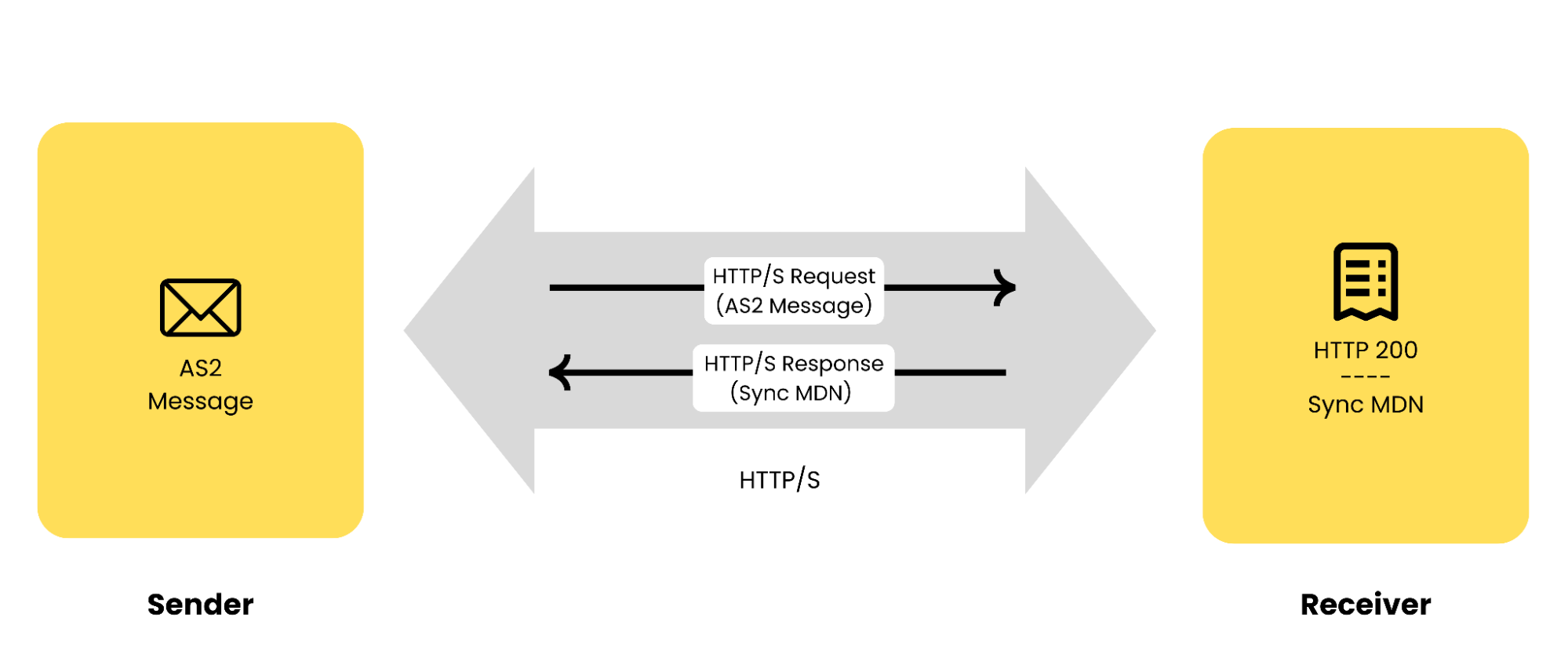
Synchronous MDNs (Sync MDNs)
A synchronous MDN is sent back to the sender within the same HTTP/S exchange that was used to transmit the original AS2 message. Sync MDNs are faster because they use the same HTTP/S connection, making them ideal for situations where low latency and immediate feedback are essential.
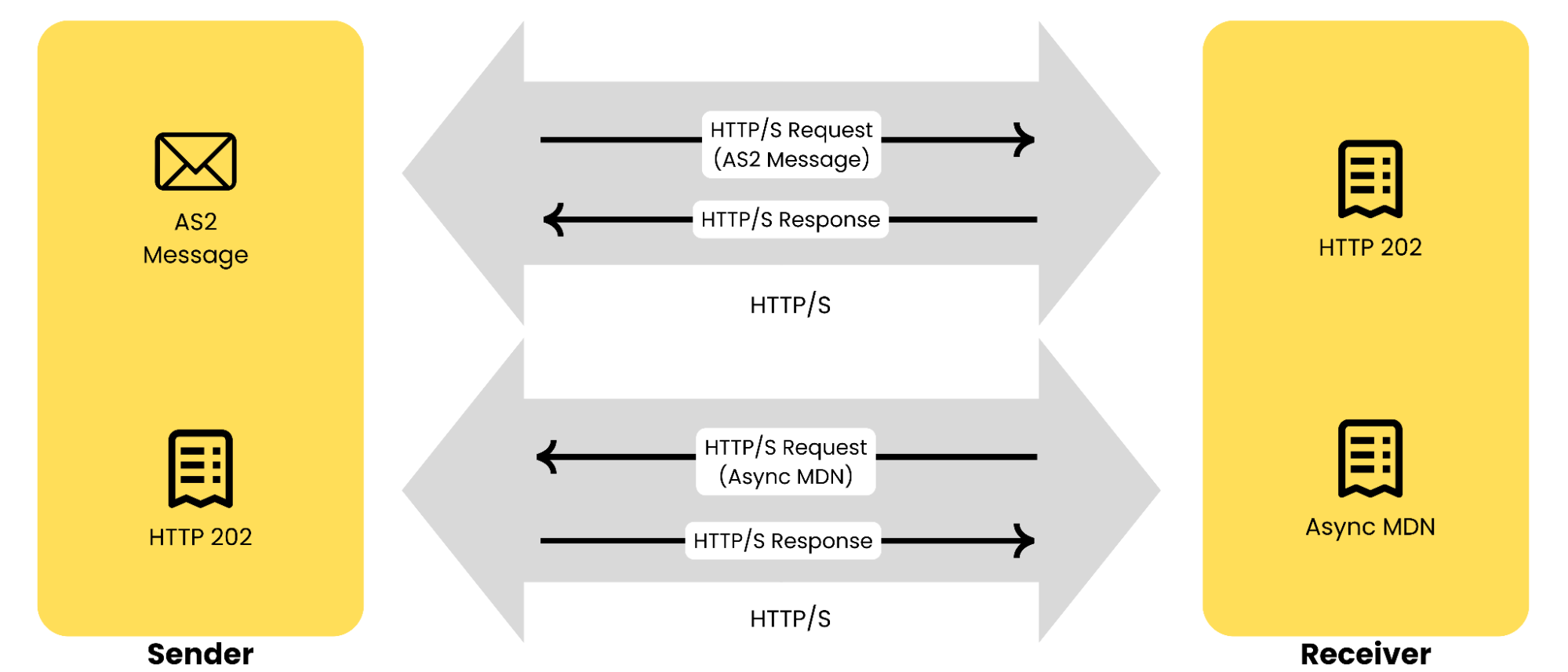
Asynchronous MDNs (Async MDNs)
An asynchronous MDN is sent back to the sender in a separate HTTP/S exchange. This method is used when dealing with large files or high latency on the partner’s side, where immediate acknowledgment is not feasible.
How to Request an MDN According to AS2 Protocol Requirements
Requesting a Message Disposition Notification (MDN) is an important step to ensure secure and reliable file transfers in AS2 communication. Platforms like MFT Gateway or AS2 Gateway make this process easier, and it’s crucial to configure the settings properly to meet protocol requirements and the expectations of trading partners. Below is a detailed guide to requesting an MDN using these Platforms.
Steps to Request an MDN
Configure AS2 Settings to Request an MDN
In platforms like MFT Gateway or AS2 Gateway, you can specify that an MDN is required for all outgoing messages. This ensures that the recipient will generate and send an acknowledgment after processing the AS2 message.
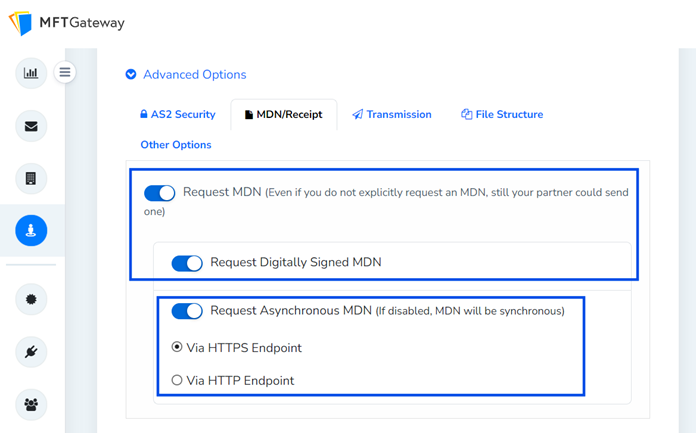
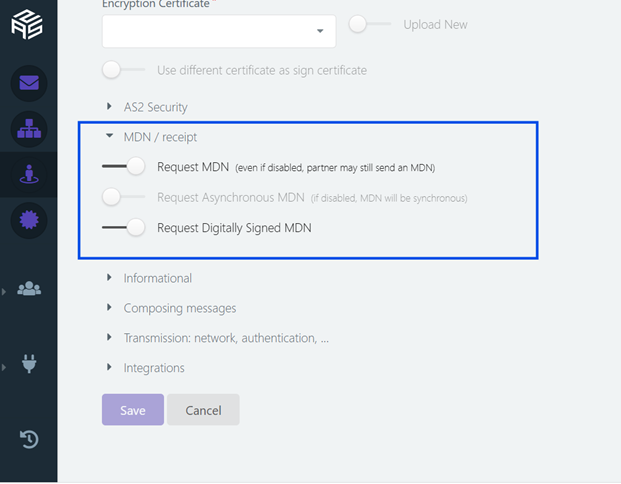
You can also specify whether the MDN should include a digital signature for added security.
Most AS2 platforms offer an option to request MDNs in their configuration settings, so make sure this option is enabled.
Specify the Type of MDN (Sync or Async):
Choose between a synchronous (sync) or asynchronous (async) MDN based on your business needs. This preference is specified in the AS2 headers of the outgoing message.
-
Sync MDN: For immediate acknowledgment within the same HTTP/S exchange.
-
Async MDN: For delayed acknowledgment in a separate HTTP/S exchange.

Simplify your AS2 connections and make B2B communication faster, safer, and easier than ever.
Conclusion
MDNs are a key part of AS2 communications, providing important acknowledgments that ensure secure and reliable message delivery as well as data integrity. By configuring your system to request MDNs and adding digital signatures, you ensure messages are both delivered and verified, building trust between trading partners. Whether using synchronous or asynchronous MDNs, each serves a specific purpose, offering flexibility in your communications.

Talk to an EDI Expert
Join hundreds of organizations already taking full control of their B2B AS2 communications with our trusted solutions. Contact us today to tailor a solution that fits your specific AS2 EDI needs.
Related Articles
View All BlogsExplore our product stack
Try before you buy with a 30-day Free Trial
No commitment, all value. Try the AS2 Solution Risk-Free and discover how our solutions can transform your business workflows. No credit card required.
Explore Your Possibilities
Elevate AS2 Communications with our EDI and AS2 Solutions
See how our AS2 and EDI solutions can simplify your integrations, boost efficiency, and keep you compliant—request a personalized demo today.