MFT Gateway is a hosted Software as a Service (SaaS) solution that enables file exchange over the AS2 or SFTP protocol, without the need to install or maintain.
- Blog
- Types of EDI
EDI
Types of EDI
In our latest blog post, we've shared details about the different types of EDI. Dive in to expand your knowledge

Kumudika Rupasinghe
Published: 18 Aug 2022

EDI or Electronic Data Interchange is a computer-to-computer communication mechanism for exchanging business documents such as purchase orders, and invoices in a standard electronic format, as an alternative to traditional paper-based communication. There are many different types of EDI and trading partners are free to interact directly using Direct EDI or through an intermediary such as EDI via AS2, and EDI via SFTP. Out of all the options, every organization should select the best way to send and receive trading documents. Therefore, before investing in EDI infrastructure, better to assess the organization’s business requirements, resource availabilities, technical capabilities and budget allocations. And most importantly, organizations should select an EDI communication option which is strategically and tactically aligning their business requirements and increases efficiencies in the supply chain to allow organizations to gain a competitive advantage over their competitors. Therefore, it is essential to look into each EDI type separately.
👉 New to EDI? Do not worry. Click here to explore our EDI blog posts to learn more about EDI
Direct EDI: Point-to-Point/Peer-to-Peer
Direct EDI; a.k.a Point-to-Point EDI/ Peer-to-Peer EDI is where trading partners connect directly to each other establishing a single secure connection between the two entities. In this approach, the organization set up separate connections between each trading partner and connects directly via the internet using the mutually agreed EDI protocol. Since no intermediaries are involved, the organizations have more control over their communication channels and out of the other options, this is the most secure form of EDI communication in general. This EDI type is most commonly used by large corporations such as Walmart that exchange a high volume of EDI documents, frequently with their trading partners.
However, since the organization sets up individual connections with the trading partners, this EDI type can become complex and resource-intensive. Normally, different EDI trading partners use separate EDI protocols, languages and EDI standards when communicating with the corresponding trading entity. Normally, this is the general practice in EDI trading. Therefore, the system should have the potential to support all of those protocols, languages and EDI standards. It might be costly for the organisation since they have to map each trading partner separately. Large organizations like Walmart might have to manage thousands of separate EDI connections and they may even need a dedicated technical team with the expertise to handle these EDI configurations and maintaining such an in-house team with the right expertise is indeed a challenge. For the organizations that don’t have the right in-house team, this option may not be the best fit.
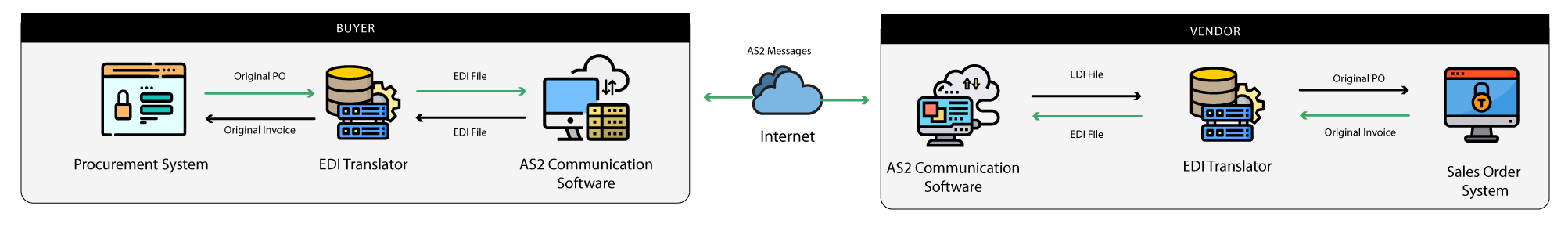
EDI via AS2
This is one of the most popular methods out of all the EDI types and Walmart is one of the main organizations that uses AS2 for its EDI communications. AS2 behaves as an “envelope” for the EDI data, enabling a better way to send and receive data securely and directly using digital certificates and encryption via the internet using HTTP connections through a certified server.
Not only EDI, but AS2 can also handle any type of file format and mandate message disposition notifications (MDNs) as an acknowledgement for the organization when a document has been accepted by the corresponding trading partner. According to the technical behaviour of AS2, it requires an active server on the message receiver’s end that listens for messages sent to it. If the receiving organization’s server is not available at the moment the message has been transmitted, according to the AS2 specifications, the sender’s trading system will retry the message, so the receiver won’t miss the message.
There are many service providers in the market that offer EDI via AS2 and due to the secure transmission, simplicity and cost-effectiveness, AS2 is considered by many organizations as the best way to communicate with EDI trading partners.
EDI via VAN
Instead of managing multiple EDI direct connections, an organisation can opt for an EDI VAN (value-added network), which is a secure network that provides partner connections and efficiently delivers EDI transactions through a single connection. The EDI VAN provider will provide a mailbox for each organization where the EDI documents are sent and received. Normally the service provider will enable alerts for incoming messages or organisations can periodically check this mailbox to retrieve received EDI documents. Similar to incoming messages, once a message is successfully sent, the organization will be notified about that as well.
When the organization has to manage a large number of different relationships within the supply chain, this option would be more efficient and cost-effective compared to Direct EDI because of the centralized system with multiple connectivity options and flexibility to expand, support of multiple protocols, fast message delivery, etc. However, this will reduce the degree of control since a third-party VPN provider is involved and the organization has to ensure all the trading partners support EDI via VPN.

EDI via SFTP, FTPS
This EDI type provides point-to-point connectivity to organizations to enable secure file transferring between networked hosts. Here the organization sends and receives EDI documents with a direct SFTP/FTPS connection established with the EDI trading partner or as well as via EDI network service providers. This method can be considered secure and reliable. However, non-repudiation and interoperability are not addressed by this method.

Web EDI
In Web EDI, EDI communication is conducted through a browser. Here a web form will contain fields where users can enter information. Once the user adds all the required information to the form, it will be automatically converted into an EDI message. Then it will be sent via secure internet protocols like AS2, HTTPS and FTPS. Because of the simplicity, Web EDI can be used to communicate with all business partners including small and medium-size businesses where technical expertise is lacking. Since it is completely browser-based, the organisations don’t have to worry about the complex installation and maintenance of EDI software.
The Foundation of Web EDI is the ‘hub and spoke’ model, where the main organization perform as the hub and the small business partners of that organization act as the spokes. Here, the main organization implements EDI and develops a web application where the small business partners can connect to that application via web browser and fill in data. Then those data will be converted to EDI documents and transmitted to the main organization.
Summary
There are several EDI types in the market and each one has its own set of benefits and drawbacks and suitability for the different business cases. Therefore it is essential to find out which EDI type is more suitable for the organization. Most of the time organizations are unable to find one solution which’s the best fit for their organization out of the available EDI types. Therefore, unlike sticking to one EDI solution, many larger organizations go for hybrid solutions according to the required volume, frequency of transactions, importance, etc. Therefore, the success of the implementation depends on the selection of the right implementation.
👉 Do EDI Better, Send and receive EDI files like emails. Sign up Today!

Talk to an EDI Expert
Join hundreds of organizations already taking full control of their B2B AS2 communications with our trusted solutions. Contact us today to tailor a solution that fits your specific AS2 EDI needs.
Related Articles
View All BlogsExplore our product stack
Try before you buy with a 30-day Free Trial
No commitment, all value. Try the AS2 Solution Risk-Free and discover how our solutions can transform your business workflows. No credit card required.
Explore Your Possibilities
Elevate AS2 Communications with our EDI and AS2 Solutions
See how our AS2 and EDI solutions can simplify your integrations, boost efficiency, and keep you compliant—request a personalized demo today.