MFT Gateway is a hosted Software as a Service (SaaS) solution that enables file exchange over the AS2 or SFTP protocol, without the need to install or maintain.
- Blog
- Two-Way TLS/SSL Authentication (mTLS): Why It Matters & How MFT Gateway Simplifies It
MFT
Two-Way TLS/SSL Authentication (mTLS): Why It Matters & How MFT Gateway Simplifies It
Learn how mutual TLS (mTLS), also called two-way TLS authentication, protects sensitive data by verifying both client and server identities. Explore key benefits, implementation challenges, and how tools like MFT Gateway simplify certificate management, handshake troubleshooting, and secure transmissions.

Dinuka Ekanayake
Published: 23 Sep 2025

In today’s business world, data security is the most important factor when exchanging business documents or other sensitive data between partners across networks or cloud platforms. TLS/SSL security is a standard technology that plays a major role in data exchange by ensuring secure communications, encrypting traffic, and verifying server identities. However, in many transmissions, validating only the server side of the connection is not enough. This is where Two-way TLS Authentication, also known as mutual authentication, is required, as it verifies both client and server before exchanging files for stronger security. In this blog, we discuss what Two-way TLS Authentication is, how it differs from one-way authentication, and how tools like MFT Gateway handle these technologies.
Understanding TLS/SSL Authentication
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is an encryption protocol and the base of secure communication over the internet. TLS is the improved and more secure version of SSL (Secure Socket Layer) and ensures that data is encrypted when exchanged between a client and a server. Both the client and server need to verify each other’s identity before sharing data to maintain secure communication. In most cases, this process uses digital certificates issued by trusted Certificate Authorities.
In TLS authentication, there are two common setups: one-way authentication and two-way authentication.
The most commonly used form is one-way authentication. In one-way authentication:
- The client initiates a secure connection.
- The server responds by presenting its certificate.
- The client verifies that certificate against its list of trusted authorities, checking details like validity period and the certificate chain.
- If valid, the session continues, and the client and server communicate further for actual data transfer with encryption.
Here, the client only authenticates the server. However, the server does not verify the client in return.
In two-way TLS authentication, also known as mutual authentication, the process involves more steps than one-way authentication. In two-way authentication, as in one-way authentication:
- The server still presents its certificate for validation by the client.
- Additionally, the server requests a client certificate.
- The client presents its certificate, which the server validates against its own trusted CA chain.
- Only if both sides successfully validate each other’s certificates, a secure, encrypted session can be established.
This initial process that establishes a secure, encrypted, and authenticated channel between a client and a server before exchanging actual data, is also known as the TLS Handshake.
Why Two-Way TLS Security Matters
In a one-way TLS setup, the client validates the server, but the server doesn’t validate the client in return and accepts any client that can establish a TLS session. This scenario can introduce a potential risk, where an unauthorized or malicious client could still connect and attempt to send data.
The additional steps in two-way TLS authentication create a more secure communication between the client and server. Not only does the client know it is connecting to the correct server, but the server also verifies that it is communicating with an authenticated, authorized client. This prevents network attacks and stops unauthorized devices from connecting to the server.
Challenges with Implementing Two-Way TLS
Although Two-way TLS authentication offers many advantages, there are a few challenges when implementing it. Here are some common challenges that business parties may face.
Certificate Management In Two-way authentication, each client needs a valid digital certificate to establish a connection with the server. Therefore, each business party must issue, distribute, and manage these certificates, including tracking expiration dates and renewing them on time.
Configuration Complexity Both the server and client applications must be correctly configured to initiate a connection with each other. Additionally, some applications may not support two-way authentication or may be incompatible with certain TLS versions, cipher suites, or certificate formats.
Troubleshooting Difficulties While establishing the connection, handshake failures can occur due to various reasons, including untrusted client certificates, TLS version mismatches, and missing client certificates.
How MFT Gateway Simplifies Two-Way TLS
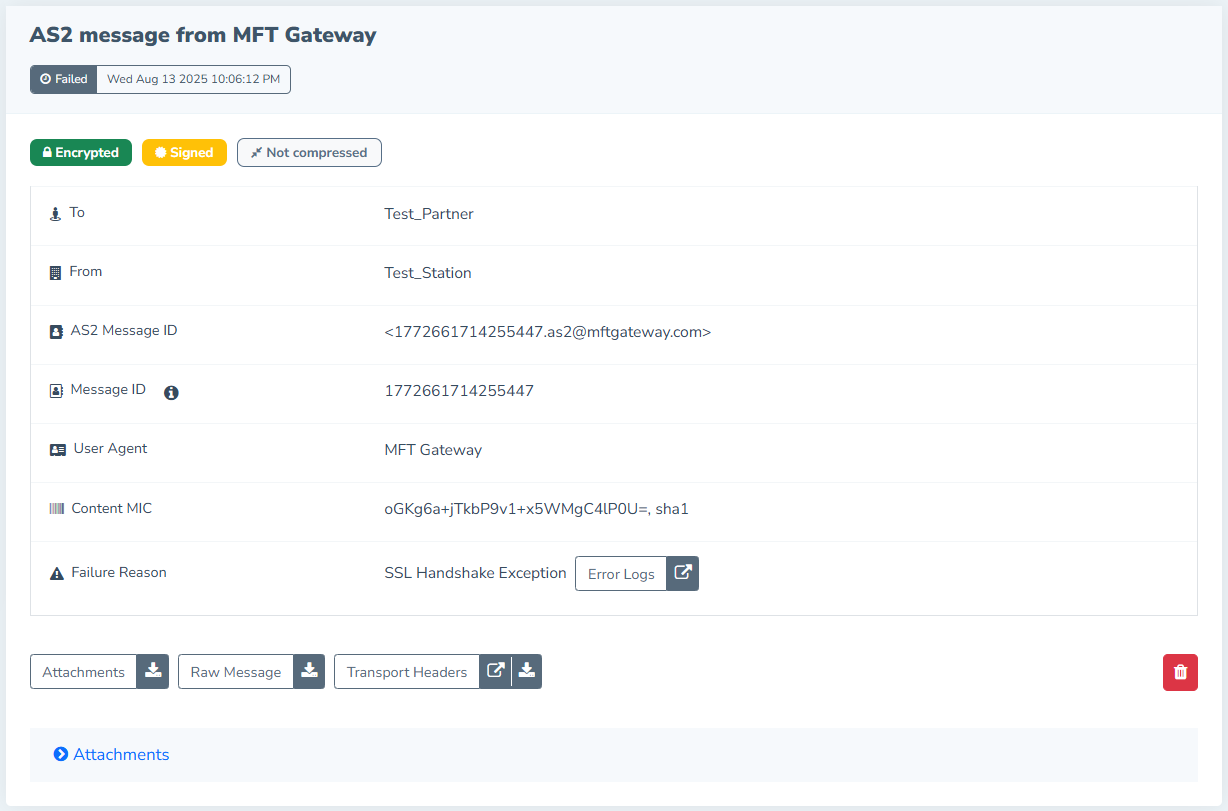
In MFT Gateway, these challenges in implementing TLS connections are addressed through features like certificate management and Station Partner Management options. It also provides error logs and detailed message information when a handshake failure occurs, making it easier to troubleshoot the errors.
In the Certificate Management view in MFT Gateway, users can create an “HTTPS (SSL/TLS) Keypair” required for two-way authentication and add it to the MFT Gateway identity store. These created certificates can be assigned to the Station representing the organization, under the “Manage Station” view in MFT Gateway.
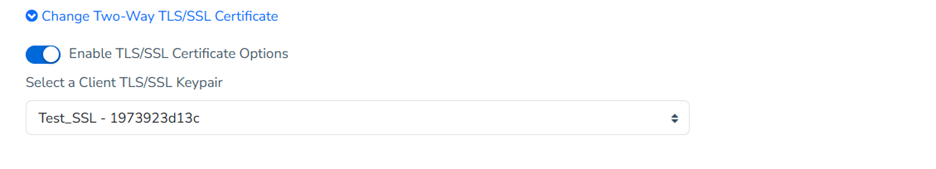
The “Manage Partner” view also provides an option to assign a partner HTTPS (TLS/SSL) certificate for two-way authentication.
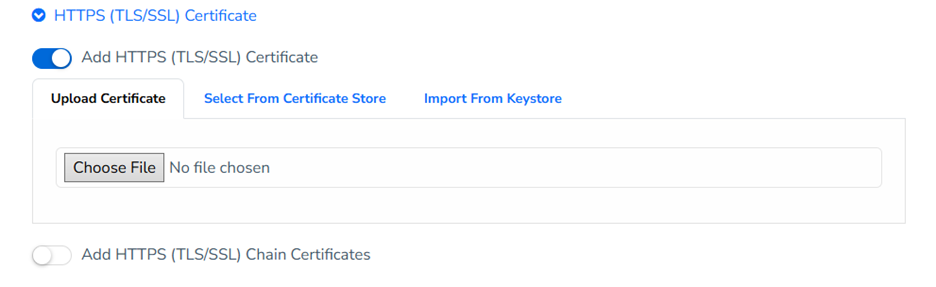
Also in MFT Gateway, if a message fails to send due to handshake errors, it is moved to the Failed list, allowing users to identify unsuccessful transmissions. Each failed entry shows the reason for failure, with additional details in the Error Logs section, including timestamps, and specific error messages.
Conclusion
Two-way TLS security provides a more secure method than one-way TLS for organizations transmitting sensitive data. It is essential for protecting file transfers, preventing unauthorized access, and ensuring compliance with industry standards. By verifying both client and server identities, mutual authentication provides a level of trust that one-way TLS cannot offer. Tools like MFT Gateway simplify this process by providing certificate management features and clear logs with message details, making it much easier to troubleshoot problems quickly and ensuring smoother, more reliable file transfers.

Talk to an EDI Expert
Join hundreds of organizations already taking full control of their B2B AS2 communications with our trusted solutions. Contact us today to tailor a solution that fits your specific AS2 EDI needs.
Related Articles
View All BlogsExplore our product stack
Try before you buy with a 30-day Free Trial
No commitment, all value. Try the AS2 Solution Risk-Free and discover how our solutions can transform your business workflows. No credit card required.
Explore Your Possibilities
Elevate AS2 Communications with our EDI and AS2 Solutions
See how our AS2 and EDI solutions can simplify your integrations, boost efficiency, and keep you compliant—request a personalized demo today.