MFT Gateway is a hosted Software as a Service (SaaS) solution that enables file exchange over the AS2 or SFTP protocol, without the need to install or maintain.
- Blog
- Why is multi-factor authentication important in B2B transactions?
AS2
Why is multi-factor authentication important in B2B transactions?
Learn about the importance of multi-factor authentication (MFA) in B2B transactions. Read our latest blog.

Indunil Rajapakse
Published: 26 Aug 2024
Businesses must prioritize digital interaction security to protect sensitive data and preserve confidence with the parties involved in business transactions. Selecting the correct B2B transaction solution featuring advanced security features, such as multi-factor authentication, lowers the risk of unauthorized access. This layer of protection, especially for sensitive data regions, should be required, with users providing two or more verification factors. Adding multi-factor authentication to online and mobile applications is quick and simple, satisfying industry regulatory standards and guaranteeing user trust verification—all without putting you in trouble for native system development and maintenance.
What are the famous user authentication methods?
The demand for multiple user authentication technologies is increasing for access control and business development, highlighting the necessity for a variety of authentication techniques. Before allowing access to a service, an authentication technique verifies the identity of the user.
-
Single-factor authentication: It requires only one type of authentication, making it simple for hackers to exploit. Simple passwords can be readily cracked using personal information or bots. Therefore, this is a frequent method for cybercriminals to obtain access to user accounts. While single-factor authentication can work well with a strong password, it is not as secure as multi-factor authentication solutions.
-
Two-factor authentication (2FA): This requires just two authentication elements. Login credentials are the first factor, and an additional method of your choosing is the second.
-
Multi-factor authentication (MFA): The method is an electronic authentication procedure that requires users to provide two or more verification factors in addition to their login credentials when accessing their resources.
What is Multi-factor authentication (MFA) ?
MFA is a security feature that requires multiple forms of authentication to lessen the likelihood of unauthorized access. This strategy adds additional levels of security to resist sophisticated internet attacks, as login information can be stolen, revealed, or sold by unauthorized parties.
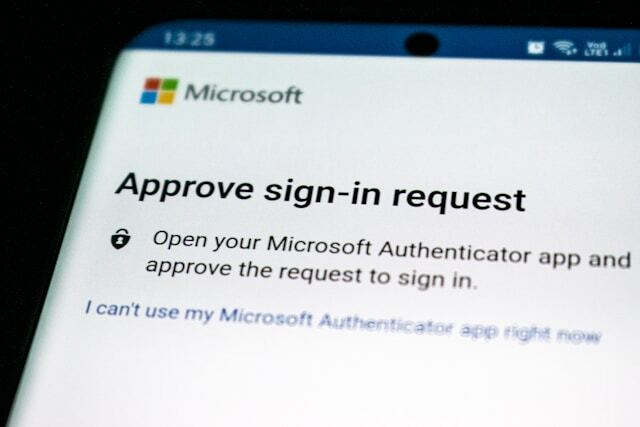
When an end-user connects to an account, as usual, they enter their username and password. They will next be requested to authenticate their identity, with several choices available. Users may be required to answer a secret question, scan their fingerprints, or enter a code received via their pre-configured email address, phone number, or authenticator application.
Unlike single-factor authentication, MFA authenticates a user’s identity by combining verification methods from at least two distinct categories of authentication factors. MFA authentication methods, safeguard customer accounts, and organizations can use any or all of these methods depending on their needs.
Why is MFA so important?
As more businesses transition to digital transformation, cybersecurity becomes increasingly vital, and corporations need to understand why MFA is so important. MFA is especially significant because it provides enhanced and appropriate security against theft and harm to a company’s critical data. Secure passwords are common for online identity authentication, although they provide limited protection.
Consumers frequently use weak passwords or reuse the same password for several applications, making it simple for attackers to obtain credentials. Attackers may access databases, encrypted or not, and expose critical information.
As a result, MFA is critical, necessitating further security checks even if unlawful access is granted. MFA codes are less vulnerable to phishing attempts because they are usually time-sensitive and non-reusable. MFA uses one-time passwords (OTP), which are 4–8 digit codes received via email, SMS, or mobile apps. OTPs generate a new code either periodically or each time an authentication request is submitted.
Meets regulatory compliance
MFA is regarded as a crucial control in almost every compliance guideline. It helps businesses protect client information. A widely accepted standard for information security management is ISO/IEC 27001. User access control is covered in Annex A.9.4.2. Ensuring users have permission to access systems and services and preventing unauthorized access are the goals of this Annex A control.
Mechanisms such as MFA can advocate limiting access to privileged utilities through authentication. A.9.4.4 highlights the necessity of ensuring that secret authentication is securely maintained, which may include MFA. Requirement 8.4.2 of the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) mandates MFA for all system components. MFA is essential for meeting industry regulations, including the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), cyber insurance providers, and President Biden’s cybersecurity executive order.
Minimizes the Risk of Password Compromises
Passwords are the most common type of authentication, yet they are also the least secure. People may reuse or share passwords, which can then be stolen or guessed. MFA ensures that even if an attacker obtains your password, they must still provide additional information to access your account.
This makes it more difficult for attackers to obtain unauthorized access to your user accounts. This is particularly helpful in situations where a system password has been compromised, and using a second method of authentication can help prevent unwanted account access.
Secure file transfer process with MFA
With years of experience, Aayu Technologies offers MFT Gateway for file transferring and EDI Generator over AS2 with EDI processing, which are trusted cloud-based systems. These systems support MFA through Aayu Accounts, the centralized user management platform for Aayu Technologies’ SaaS products.
This feature is free and optional and can be enabled or disabled according to user preferences. The user can enable the MFA feature for themselves by logging in to the Aayu User Management application’s home page.
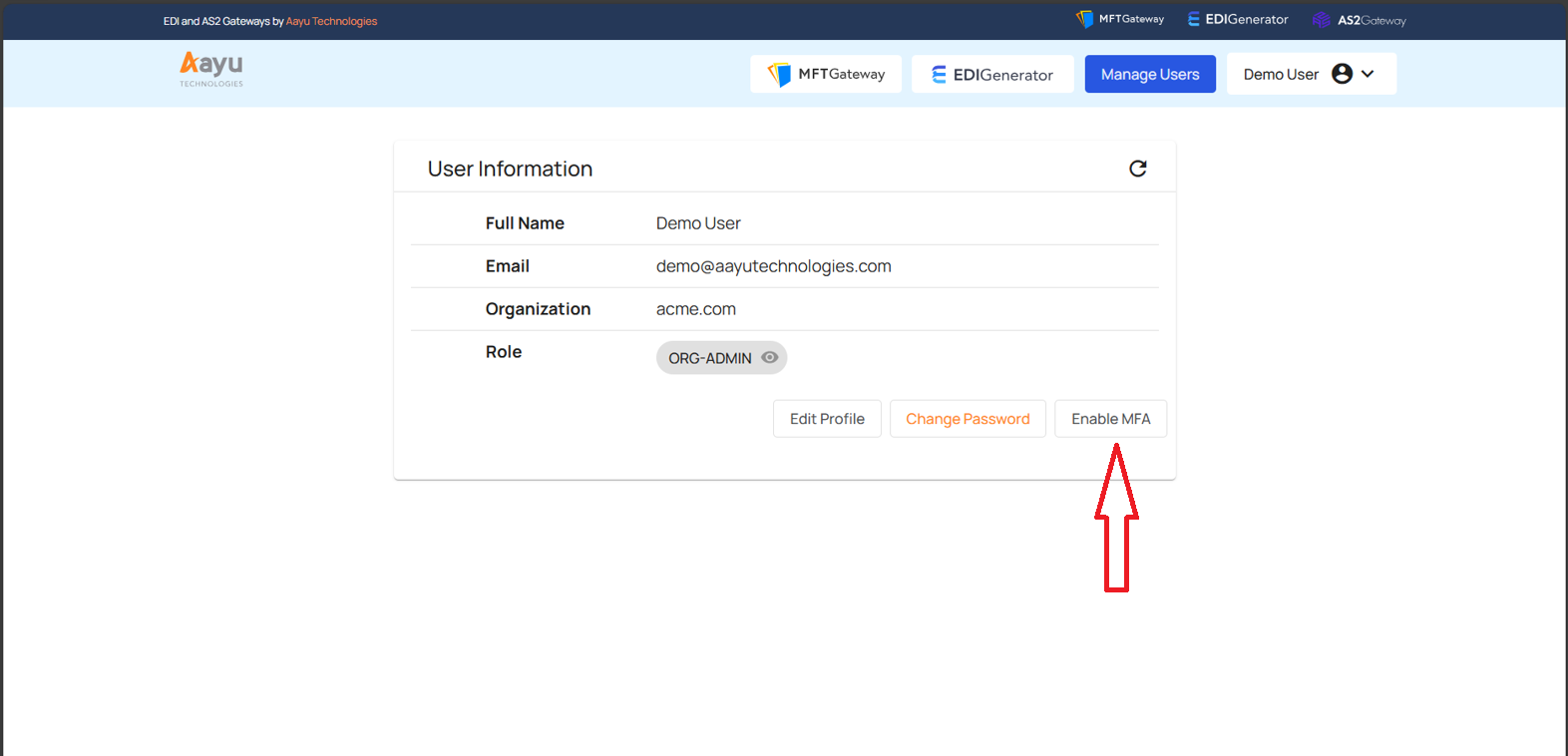
The first step outlines the considerations you should make before enabling the MFA feature. The MFT Gateway REST API integrated automation flow will break if a user activates MFA for their account, as the MFA cannot be verified via the REST API. Therefore, if you are using or are willing to use the MFT Gateway REST API integration, don’t enable the MFA to your accounts.
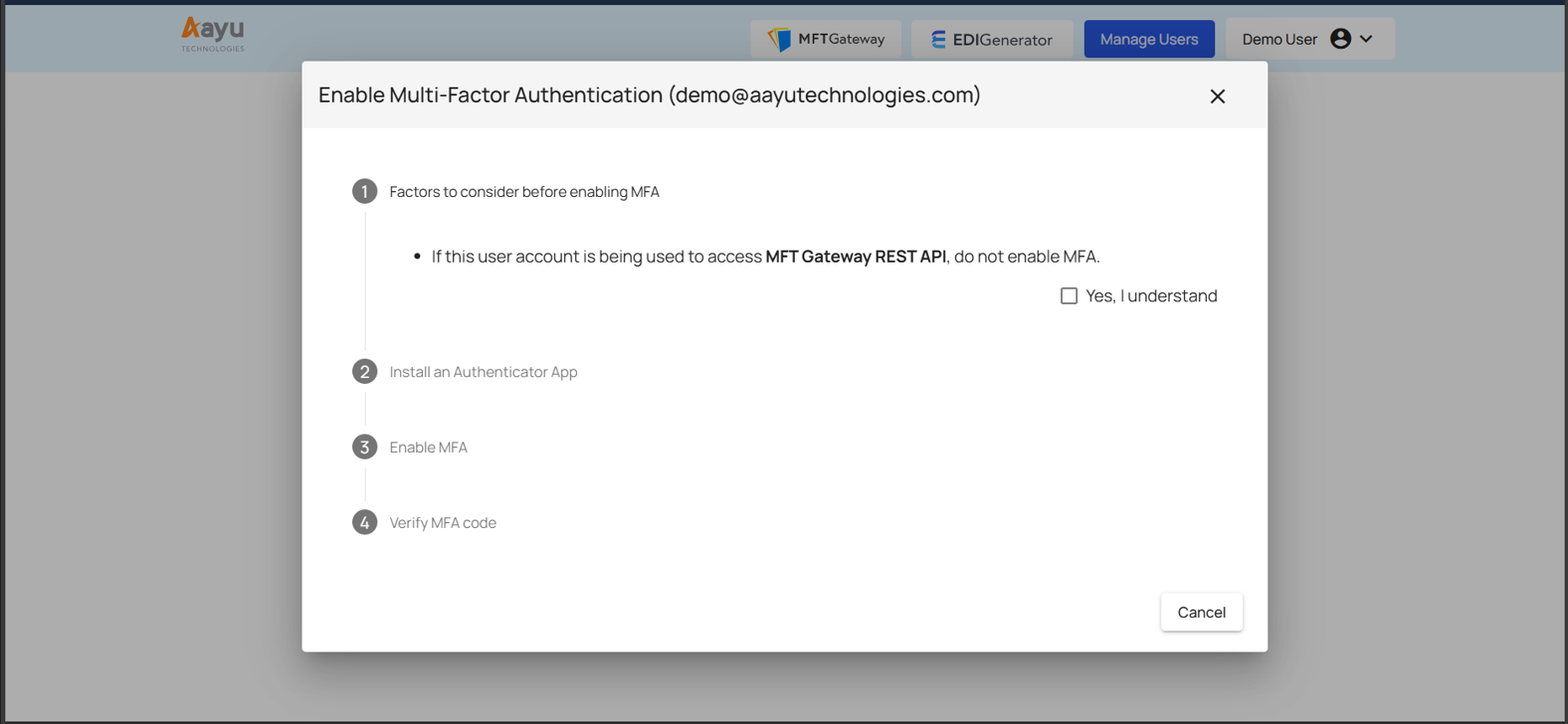
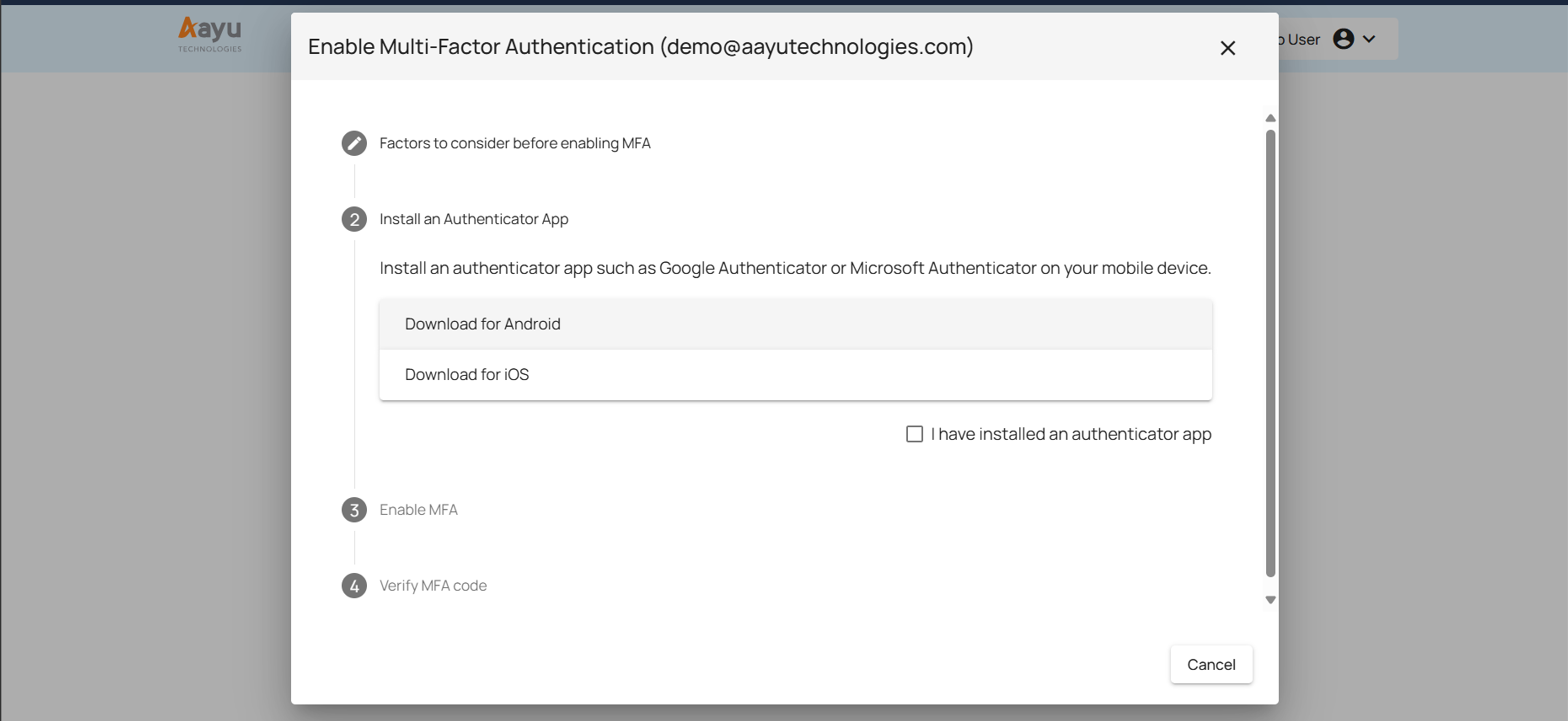
Aayu Technologies allows you to use MFA using an authenticator app, which is a simple, safe, and cost-effective solution. To utilize an authenticator app, such as Google Authenticator or Microsoft Authenticator, you must first install it on your desired mobile device, depending on the device’s mobile operating system.
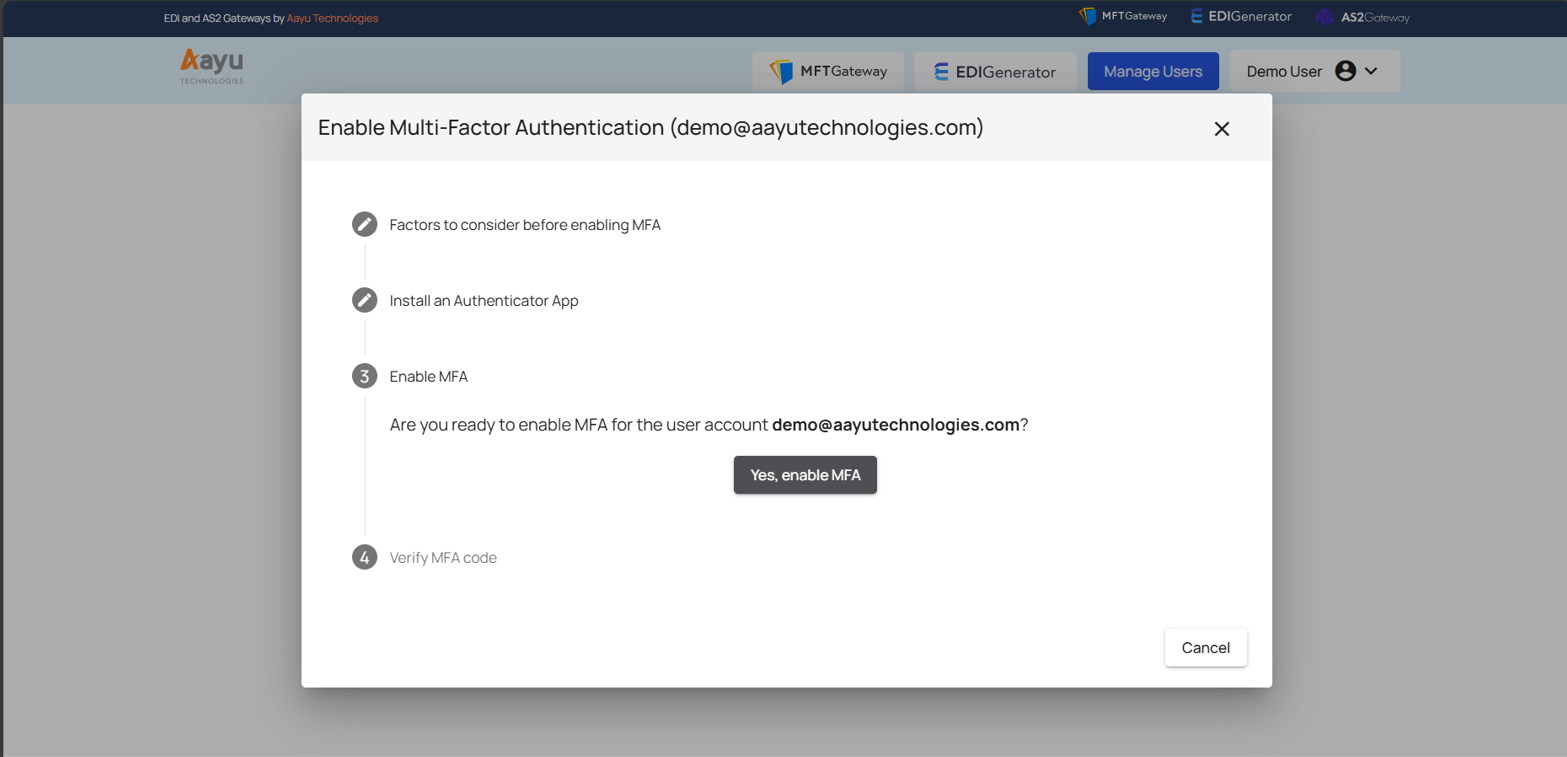
Once you are ready to enable MFA for the account, click the “Yes, enable MFA” button at Step 3.
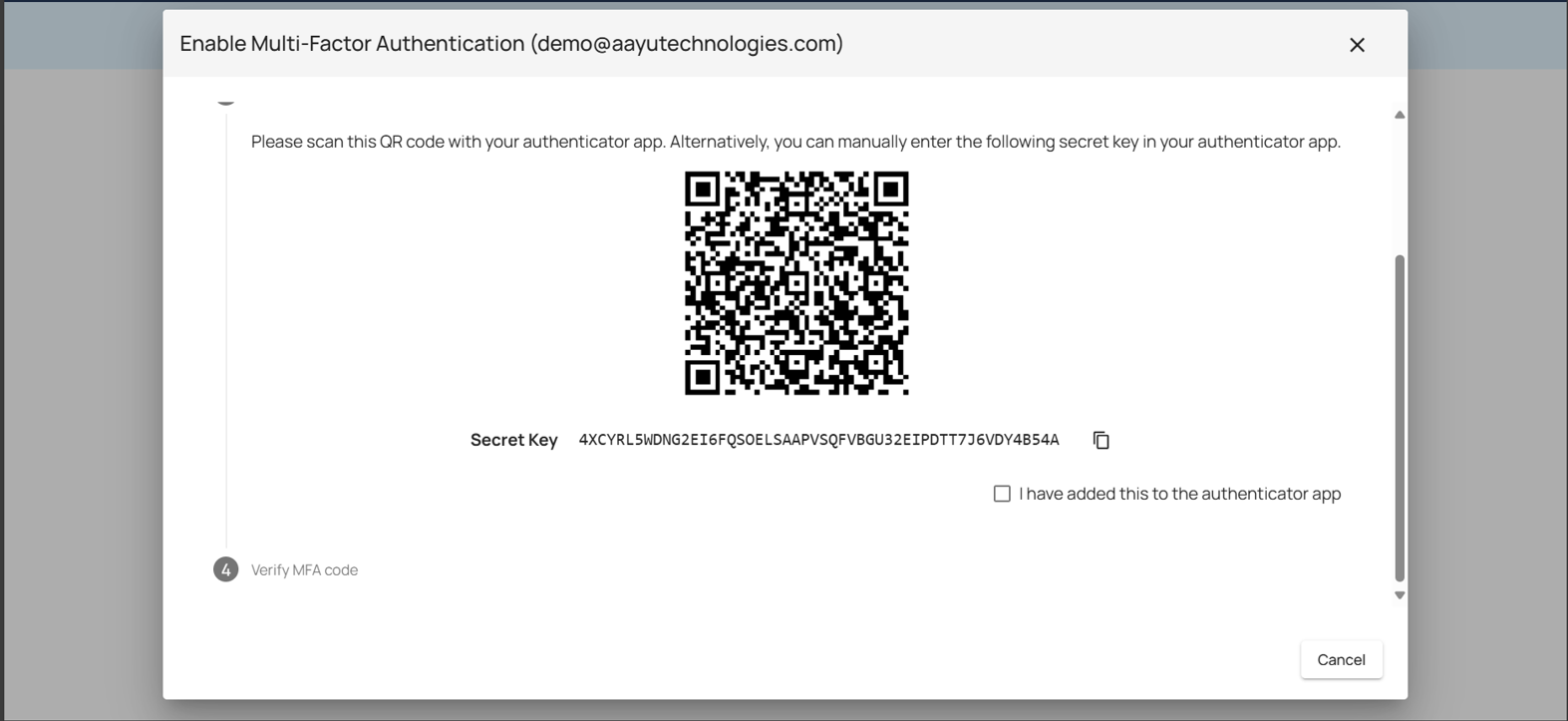
Then the users need to either scan a QR code or enter a secret key from the website using the authenticator app.
Once the user’s account has been added to the authenticator app, you must confirm it by entering the code that shows on the authenticator app issued to your account.
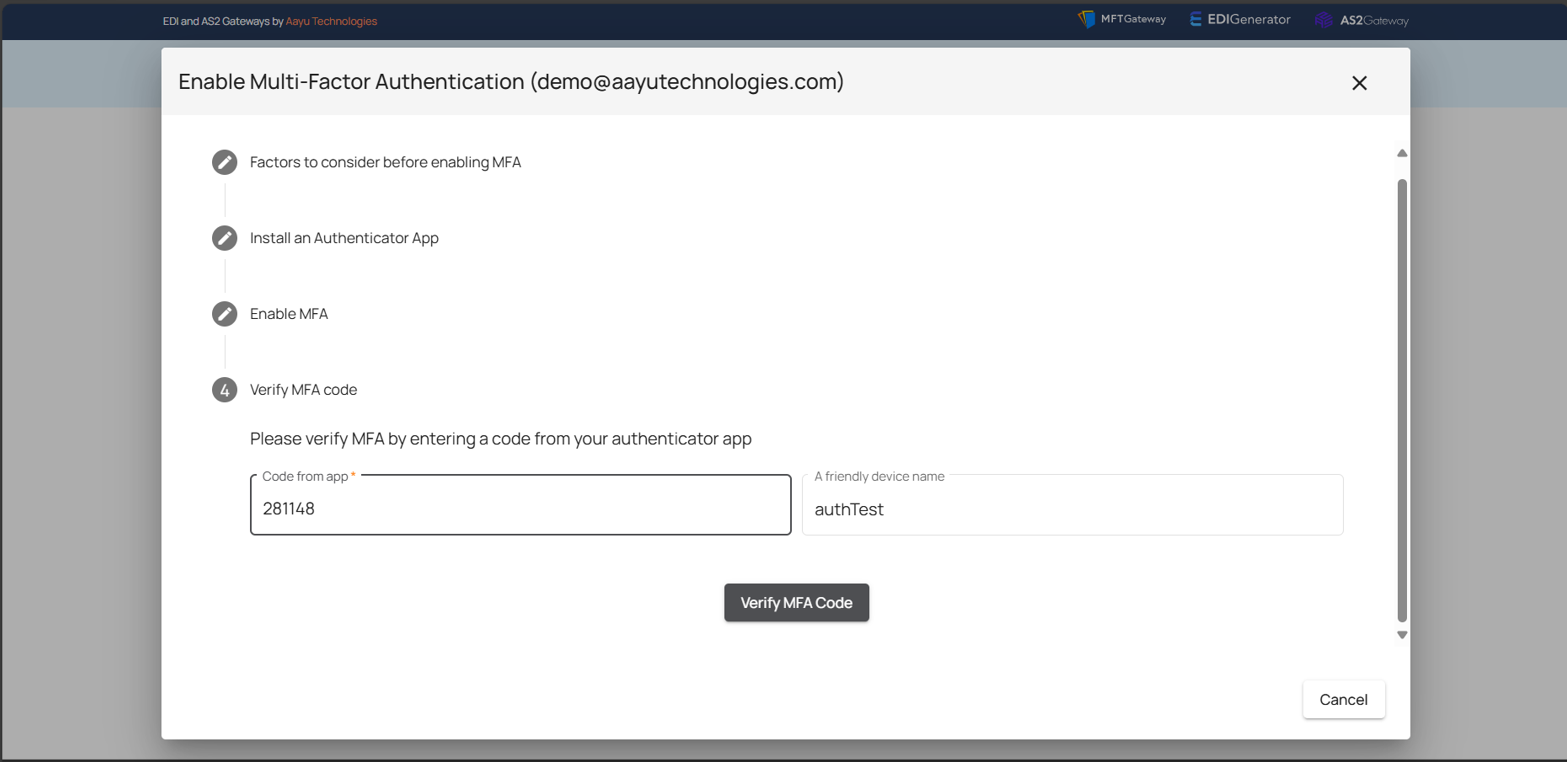
After setting up MFA by entering a code from your authenticator app, the feature will be applied to the account.
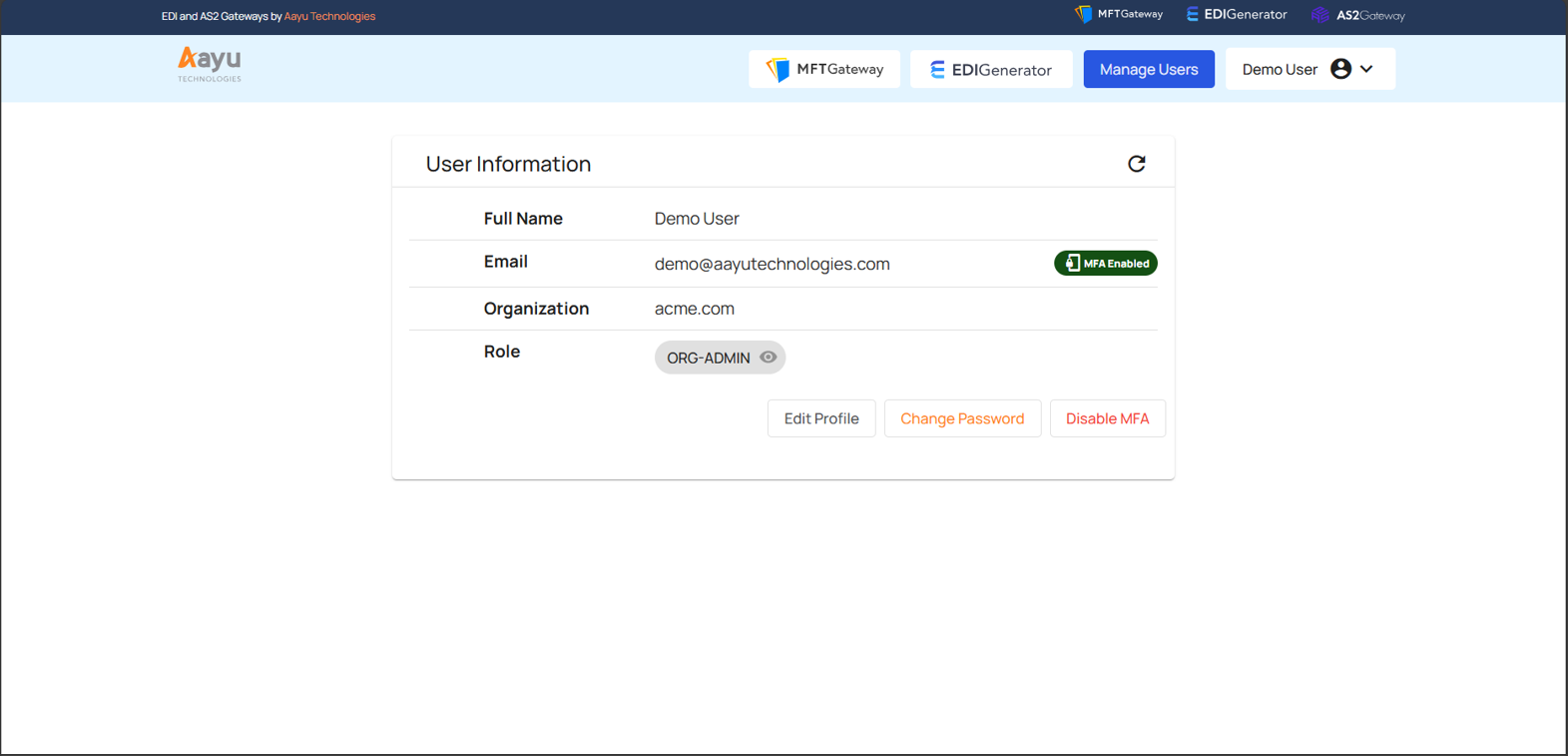
When users who have activated the MFA feature log in to the MFT Gateway, EDI Generator, and Aayu User Management applications with the correct credentials, they are redirected to a screen where they can enter the MFA code that the authenticator app generates as a one-time, time-limited password. The paired authenticator application produces code that will expire after a set amount of time.
Conclusion
MFA provides a versatile way to balance today’s security requirements with user experience. It gives you confidence that you have an additional layer of cybersecurity for your account access. In a B2B transaction system, allowing MFA is an effective way to safeguard the login process and show that you value the security of your users. Start protecting your business today with Aayu Technologies by transferring files over AS2 with EDI processing.
Talk to an EDI Expert
Join hundreds of organizations already taking full control of their B2B AS2 communications with our trusted solutions. Contact us today to tailor a solution that fits your specific AS2 EDI needs.
Related Articles
View All BlogsExplore our product stack
Try before you buy with a 30-day Free Trial
No commitment, all value. Try the AS2 Solution Risk-Free and discover how our solutions can transform your business workflows. No credit card required.
Explore Your Possibilities
Elevate AS2 Communications with our EDI and AS2 Solutions
See how our AS2 and EDI solutions can simplify your integrations, boost efficiency, and keep you compliant—request a personalized demo today.