MFT Gateway is a hosted Software as a Service (SaaS) solution that enables file exchange over the AS2 or SFTP protocol, without the need to install or maintain.
- Blog
- All You Need to Know About EDI in the Manufacturing Industry
SFTP | AS2 | EDI
All You Need to Know About EDI in the Manufacturing Industry
The manufacturing industry relies on accuracy, efficiency, and speed, making Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) vital for supply chain integration and inventory management through electronic business document exchange.

Hirudinee Liyanage
Published: 09 Jul 2024

The manufacturing industry is one of the most competitive and fast-paced industries in the world. Accuracy, efficiency, and speed have always been vital for the industry, and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) has become one of the key technologies used by manufacturers for the same reasons. EDI has been used as a tool for supply chain integration and inventory management by enabling the electronic exchange of related business documents between organizations. This blog post will discuss more on the role of EDI in the manufacturing industry, its benefits, and real-world applications.
What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a standardized set of instructions and specifications for generating documents such as purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and other important data. These EDI documents are computer-readable, and therefore the whole process can be done electronically. This eliminates the need to use traditional paper-based methods for business documents and minimizes human involvement. EDI facilitates communication between different business systems and allows the automatic transmission of information in a structured format.
Benefits of EDI in Manufacturing
Supply Chain Integration
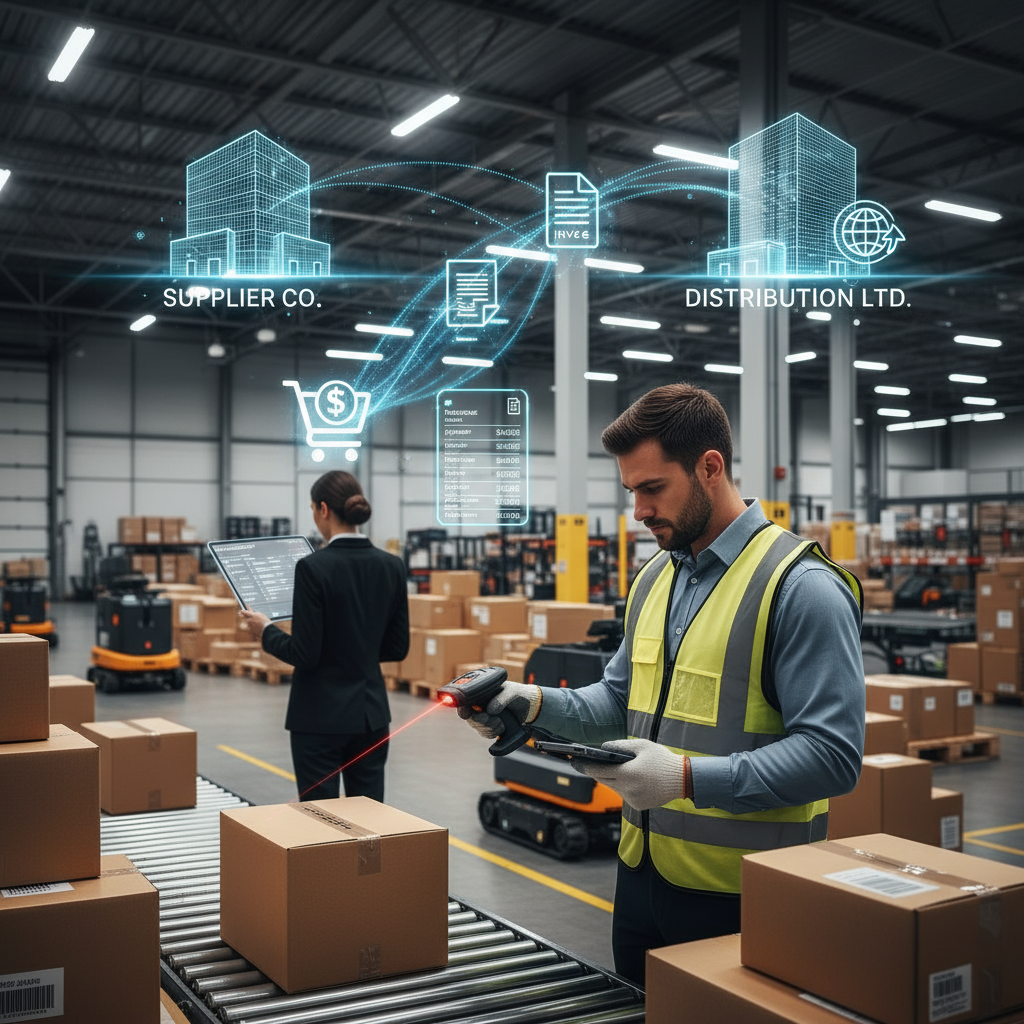
One of the key advantages of EDI in manufacturing is the integration of the Supply Chain. Once an EDI System is introduced to the organization, it enables real-time data exchange between suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. This way, businesses can enhance the collaboration between shareholders, reduce delays that naturally occur between parties, and improve overall efficiency.
Cost Savings
The use of EDI can result in significant cost savings for manufacturers. By automating the exchange of documents, EDI eliminates the need for manual data entry, reduces labor costs, and reduces the risk of human error. This will increase EDI communication speed and accuracy and also result in fewer errors that can be costly to correct. Overall, EDI helps manufacturers streamline their operations and reduce operating costs.
Improved Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is essential for the success of manufacturing. EDI provides a platform for manufacturers to see their inventory in real time, allowing them to track inventory more accurately. This visibility helps maintain optimal inventory levels, reduce overstock, and avoid stockouts. EDI allows manufacturers to implement just-in-time (JIT) inventory practices, reducing logistics costs and increasing productivity.
How EDI Works
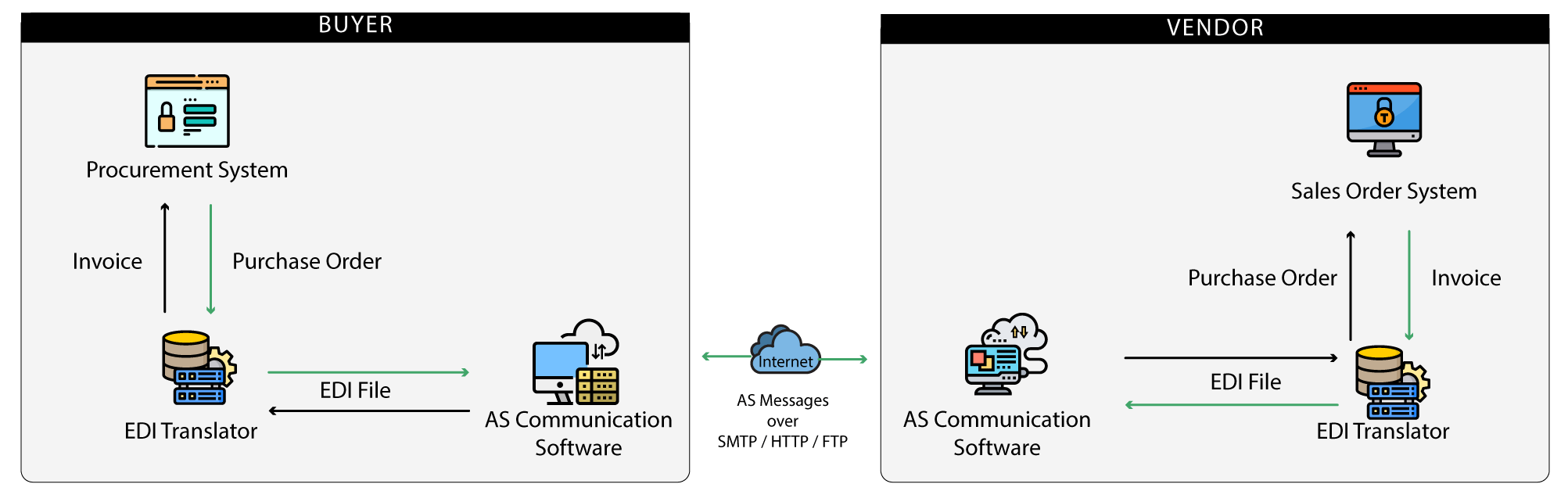
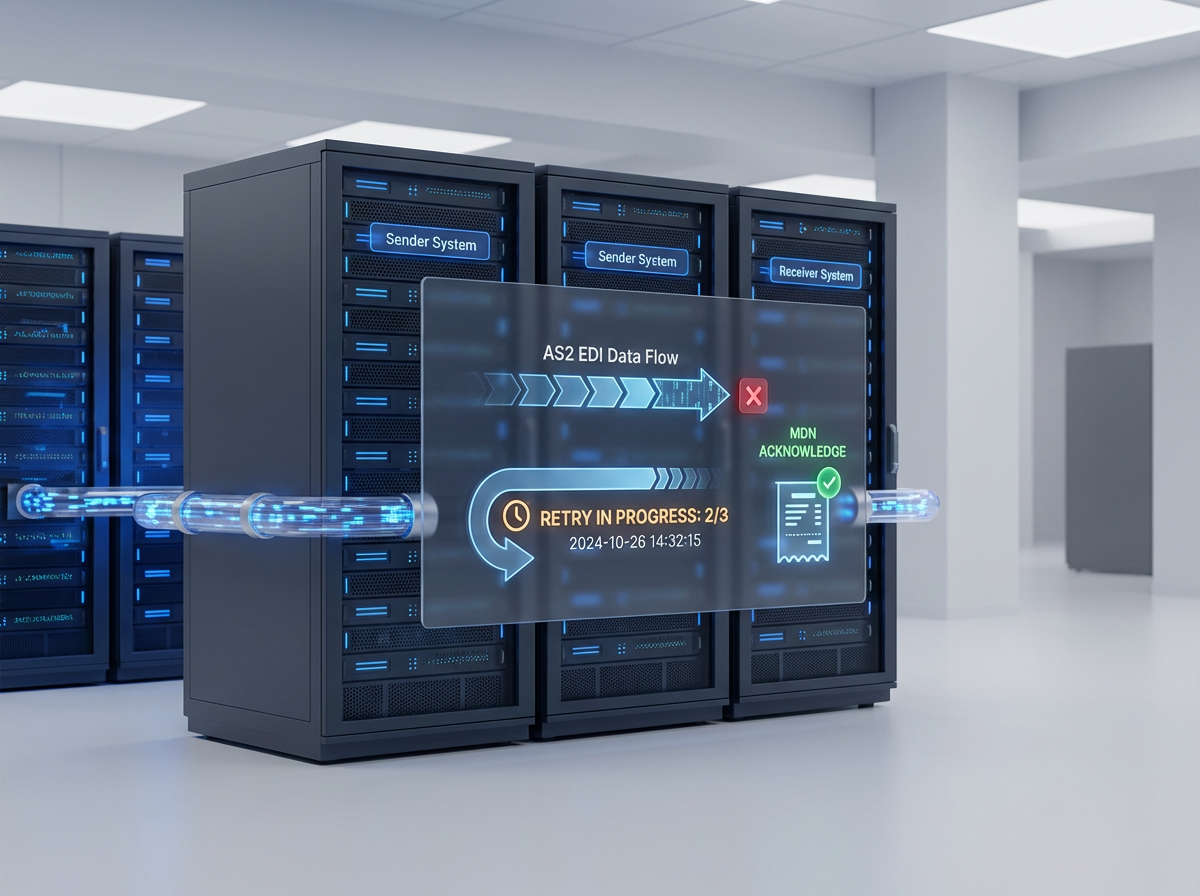
EDI operates through standardized protocols and networks that enable consistent and reliable data exchange between systems. Here is a simple overview of how EDI works in manufacturing:
1. Document Preparation: The sender’s system generates an electronic version of a business document (e.g., purchase order) in a standard EDI format.
2. Transmission: The document is transmitted electronically to the recipient’s system via an EDI network or a direct connection.
3. Translation: The recipient’s system receives the document and translates it into a format that can be processed by their internal systems.
4. Processing: The translated document is integrated into the recipient’s business processes, such as updating inventory records, generating invoices, or scheduling production runs.
EDI Standards
EDI relies on established standards to ensure consistency and interoperability of systems. Common EDI standards used in manufacturing include:
-
ANSI X12: Widely used in North America, ANSI X12 is a set of standards developed by the American National Standards Institute for various industries, including manufacturing.
-
EDIFACT: Short for Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport, EDIFACT is an international standard developed by the United Nations for global EDI communication.
-
ODETTE: Used primarily in the European automotive industry, ODETTE (Organization for Data Exchange by Tele Transmission in Europe) is a set of standards for EDI communication between automotive manufacturers and their suppliers.
Challenges and Considerations
Although EDI offers many advantages, its application in manufacturing also presents some challenges. Here are a few of the concerns that one may need to consider.
-
Initial Setup Costs: Most of the time implementing an EDI system requires an initial investment in software, hardware, and training. However, these costs are typically offset by long-term savings and efficiency gains.
-
Data Security: Ensuring the security and confidentiality of sensitive business data is critical. Manufacturers must implement strong security measures to protect their EDI communications from unauthorized access and data breaches.
-
Standardization: Adopting the right EDI standards for your business and ensuring they align with business partner policies can be challenging. Working with experienced EDI providers can help streamline this process.
There are several EDI service providers in the Marketplace right now and choosing the right solution for your business can mitigate most of the above-mentioned challenges.
Future of EDI in Manufacturing
The future of EDI in the manufacturing industry looks promising, with advancements in technology driving further innovation. Here are a few trends to watch:
-
Cloud-Based EDI: Cloud-based EDI solutions offer greater flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional on-premise systems. They enable manufacturers to quickly onboard new trading partners and adapt to changing business needs. EDI Generator is one great example of a cloud-based EDI solution.
-
Integration with IoT and AI: Integrating EDI with Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Artificial Intelligence (AI) can provide manufacturers with deeper insights into their operations. For example, IoT sensors can provide real-time data on machine performance and inventory levels, while AI can analyze this data to optimize production processes and supply chain management.

Talk to an EDI Expert
Join hundreds of organizations already taking full control of their B2B AS2 communications with our trusted solutions. Contact us today to tailor a solution that fits your specific AS2 EDI needs.
Related Articles
View All BlogsExplore our product stack
Try before you buy with a 30-day Free Trial
No commitment, all value. Try the AS2 Solution Risk-Free and discover how our solutions can transform your business workflows. No credit card required.
Explore Your Possibilities
Elevate AS2 Communications with our EDI and AS2 Solutions
See how our AS2 and EDI solutions can simplify your integrations, boost efficiency, and keep you compliant—request a personalized demo today.