MFT Gateway is a hosted Software as a Service (SaaS) solution that enables file exchange over the AS2 or SFTP protocol, without the need to install or maintain.
- Blog
- AS2 vs AS3 vs AS4: What Is the Difference Between Them?
AS2
AS2 vs AS3 vs AS4: What Is the Difference Between Them?
Learn the differences between AS2, AS3, and AS4 protocols for secure file transfer. Compare security, encryption, and features to choose the right solution for your business.

Hirudinee Liyanage
Modified: 13 Feb 2026

Table of Contents
In the world of secure file transfers, protocols like AS2, AS3, and AS4 play a major role in ensuring that data is exchanged safely between businesses. These protocols are designed to protect sensitive data, ensure compliance, and guarantee reliable delivery between trading partners. Understanding the differences between AS2, AS3, and AS4 helps organizations select the right option based on security needs, integration complexity, and scalability. This article explains how AS2, AS3 and AS4 work, compares their security, and reviews how each protocol protects data during transmission.
AS2 (Applicability Statement 2)
AS2 is the most widely used among the three protocols. Developed in the late 1990s, AS2 allows businesses to exchange data over the internet using the HTTP or HTTPS protocols. One of the biggest advantages of AS2 is that it can securely transmit almost any type of file, including documents, images, and binary data.
AS2 is especially popular in industries such as retail, healthcare, and logistics, where Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) plays a critical role. From a security perspective, AS2 uses S/MIME encryption to protect messages in transit. Messages can also be digitally signed to ensure authenticity and data integrity.
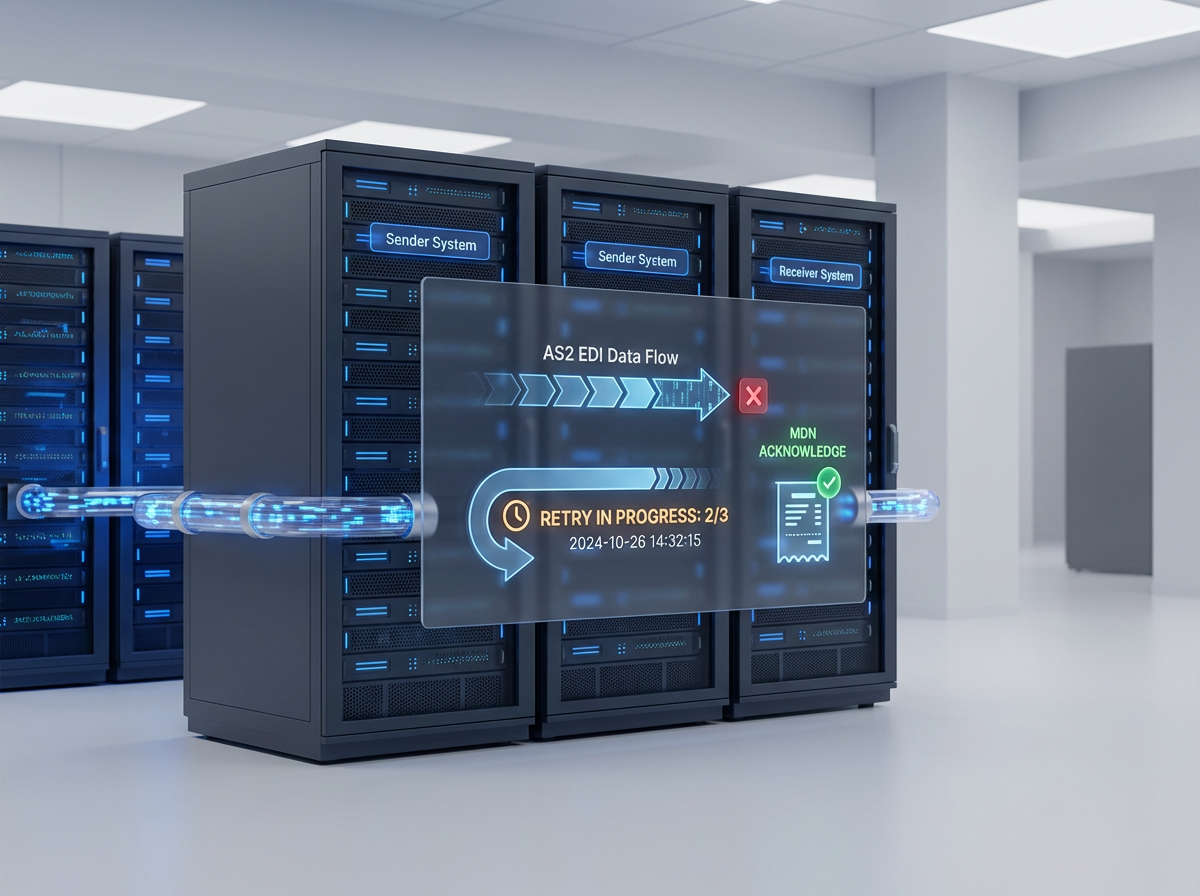
Once a message is received, the recipient sends back a Message Disposition Notification (MDN). This receipt confirms that the message was received successfully and processed without being altered. This confirmation mechanism is one of the key reasons why AS2 remains trusted for business-critical data exchange.
Another major reason for AS2’s popularity is compliance. Many regulatory frameworks require secure, auditable data transmission. In healthcare, for example, HIPAA compliance often relies on AS2 to securely exchange patient-related information.
That said, AS2 does come with some limitations. It requires a direct connection between the sender and the receiver, which can increase setup effort and ongoing maintenance, especially when managing many trading partners.
Key AS2 features include:
- Secure transmission over HTTP or HTTPS
- Strong encryption and digital signatures
- Real-time or asynchronous MDNs
- High adoption in retail, healthcare, and logistics
AS3 (Applicability Statement 3)
AS3 was developed to address some of the limitations found in AS2. The most notable difference is the transport mechanism. Instead of HTTP or HTTPS, AS3 uses FTP or SFTP for communication. This allows files to be exchanged without maintaining a constant direct connection between partners.
In practice, AS3 is an adaptation of AS2 for FTP-based file transfers. It still supports encryption and digital signatures, helping protect data during transmission. A key advantage of AS3 is its ability to handle multiple files in a single transfer, which benefits organizations with large volumes of data.
Despite these benefits, AS3 has not achieved the same level of adoption as AS2. One reason is that FTP-based protocols are often perceived as less secure, even when encryption is used correctly. In addition, AS3 does not include built-in MDN receipts, which means senders do not automatically receive confirmation that a file was successfully received and processed.
Because of these factors, AS3 is usually chosen only in environments where FTP or SFTP is already deeply embedded in existing workflows.
Key AS3 characteristics include:
- Uses FTP or SFTP for data transfer
- Supports batch and large file transfers
- Encryption and digital signatures are supported
- No built-in MDN confirmation
AS4 (Applicability Statement 4)
AS4 is the newest and most advanced of the three protocols. It is based on the ebXML Messaging Service (ebMS) standard and is designed for modern, service-oriented architectures. Compared to AS2 and AS3, AS4 offers greater flexibility and better integration with web services and APIs.
One of the standout features of AS4 is its support for asynchronous messaging. This means the sender and receiver do not need to be online at the same time. Messages can be queued and delivered when the receiving system becomes available, which is especially useful for global organizations operating across time zones.
From a security standpoint, AS4 significantly improves on earlier protocols. It uses WS-Security, which provides message-level protection for SOAP messages. This includes encryption, digital signatures, and advanced security controls that protect data both during transmission and while stored temporarily.
Key AS4 advantages include:
- Web services–based architecture
- Advanced security using WS-Security
- Asynchronous and reliable messaging
- Strong support for cloud and SOA environments
AS4 is particularly well-suited for organizations adopting cloud-based systems or API-driven integrations. However, this flexibility comes with added complexity. Implementing AS4 typically requires a stronger understanding of web services, XML messaging, and SOAP-based communication.
AS2 vs AS3 vs AS4 Security Comparison
When comparing the security of AS2, AS3, and AS4 all three protocols provide strong protection, but their approaches differ.
AS2 relies on S/MIME for encryption and digital signatures, offering confidentiality, integrity, and non-repudiation. AS3 also supports encryption, but its reliance on FTP or SFTP can introduce additional risks if configurations are not carefully managed.
AS4 takes security a step further by using WS-Security. This approach ensures end-to-end message protection, even when messages are stored, queued, or routed through intermediaries. For organizations with strict regulatory or compliance requirements, AS4 often provides the highest level of assurance.
AS2 vs AS3 vs AS4 Encryption
Understanding the encryption of AS2, AS3, and AS4 is essential when selecting a secure file transfer protocol.
AS2 encrypts message payloads using S/MIME, which has a long track record of reliability. AS3 supports encryption as well, but much of its security depends on the underlying FTP or SFTP layer. AS4 uses message-level encryption through WS-Security, ensuring that data remains protected not only in transit but also at rest.
Because of this, AS4 is often considered the most robust option when encryption and data protection are top priorities.
Choosing the Right Protocol
Choosing between AS2 vs AS3 vs AS4 ultimately depends on your business requirements.
- AS2 is ideal for organizations that need a proven, widely adopted protocol for EDI and compliance-driven data exchange.
- AS3 can work well if your infrastructure already depends heavily on FTP or SFTP and requires batch file transfers.
- AS4 is best suited for businesses looking for a modern, flexible solution that integrates easily with web services and cloud platforms.
Each protocol has its strengths and limitations. Understanding the differences helps ensure your secure file transfer strategy meets both current and future needs.
Final Thoughts
Secure data exchange is a critical part of modern business operations. Whether you choose AS2, AS3, or AS4, the right protocol can make a significant difference in security, reliability, and efficiency. Understanding the encryption methods of AS2, AS3, and AS4 is essential when selecting a secure file transfer protocol.
Once you have a clear understanding of which protocol to use in your organization, it is very important to decide how to implement these protocols. If you have an internal IT team that is capable of implementing and integrating your systems in line with the protocol requirements and providing support when issues arise, this is one possible approach.
However, most retail and healthcare-related companies choose a trusted partner like Aayu Technologies to provide expertise in AS2 and AS4 for supporting B2B communications. These providers offer a variety of options, such as SaaS or on-premise deployments, along with different pricing tiers to suit specific business needs.
Looking to implement or upgrade your secure file transfer solution? You can reach out to our expert team to find the right AS2, AS3, or AS4 approach for your business.

Talk to an EDI Expert
Join hundreds of organizations already taking full control of their B2B AS2 communications with our trusted solutions. Contact us today to tailor a solution that fits your specific AS2 EDI needs.
Related Articles
View All BlogsExplore our product stack
Try before you buy with a 30-day Free Trial
No commitment, all value. Try the AS2 Solution Risk-Free and discover how our solutions can transform your business workflows. No credit card required.
Explore Your Possibilities
Elevate AS2 Communications with our EDI and AS2 Solutions
See how our AS2 and EDI solutions can simplify your integrations, boost efficiency, and keep you compliant—request a personalized demo today.