MFT Gateway is a hosted Software as a Service (SaaS) solution that enables file exchange over the AS2 or SFTP protocol, without the need to install or maintain.
- Blog
- Considerations When Choosing a File Transfer Protocol
SFTP | AS2
Considerations When Choosing a File Transfer Protocol
Securely transfer files with advanced protocols like AS2 and SFTP, ensuring compliance, robust encryption, and seamless integration for your business needs.

Adheeb Shafik
Published: 10 Jun 2024

In the current digital environment, businesses need to thoroughly evaluate the choice of a suitable file transfer protocol. Choosing a file transfer protocol involves evaluating several key factors to ensure secure, efficient, and compliant file transfers. Let’s explore the essential FTP decision factors for businesses.
Security Requirements
FTP: Convenience vs. Security
File Transfer Protocol (FTP), developed in the early 1970s, is one of the oldest and most widely recognized protocols. Despite its historical significance, FTP doesn’t meet today’s security standards; it lacks encryption, making data transferred over FTP vulnerable to interception and unauthorized access. If your organization prioritizes convenience and compatibility over security, FTP might still be an option, especially since many trading partners continue to use it. However, it’s essential to weigh the risks of using an outdated and insecure protocol. For secure alternatives, consider protocols that offer robust encryption and authentication mechanisms.
SFTP and FTPS: Enhanced Security
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) and FTP Secure (FTPS) are two popular alternatives that address the security shortcomings of legacy FTP. SFTP uses Secure Shell (SSH) to encrypt both the command and data channels, ensuring that all communications are secure from eavesdropping and tampering. It also simplifies firewall configurations by operating over a single port.
FTPS, on the other hand, extends FTP by incorporating SSL/TLS encryption to secure the data in transit. FTPS offers flexible security modes, including implicit and explicit SSL/TLS, providing various levels of protection. While FTPS is widely supported and provides faster transfer speeds than SFTP, it requires additional ports to be opened, which can introduce security vulnerabilities.
HTTPS: Simplified Security for Non-Technical Users
HTTPS is a secure option that’s especially good for situations where ease of use is important. HTTPS leverages the widespread familiarity and accessibility of web browsers, enabling secure file transfers without the need for specialized client software. This is particularly advantageous for non-technical users who may struggle with configuring and using more complex protocols. HTTPS ensures data integrity and confidentiality through TLS encryption, but organizations should be mindful of the security policies of the service providers they choose.
Regulatory Compliance
FIPS 140-2 Compliance
For organizations that must adhere to strict regulatory requirements, such as those in the federal government or industries handling sensitive information, choosing a protocol that supports FIPS 140-2 compliance is critical. FIPS 140-2 is a U.S. government standard that specifies security requirements for cryptographic modules. Protocols like SFTP and FTPS can be configured to meet FIPS 140-2 standards, ensuring that only validated cryptographic algorithms are used.
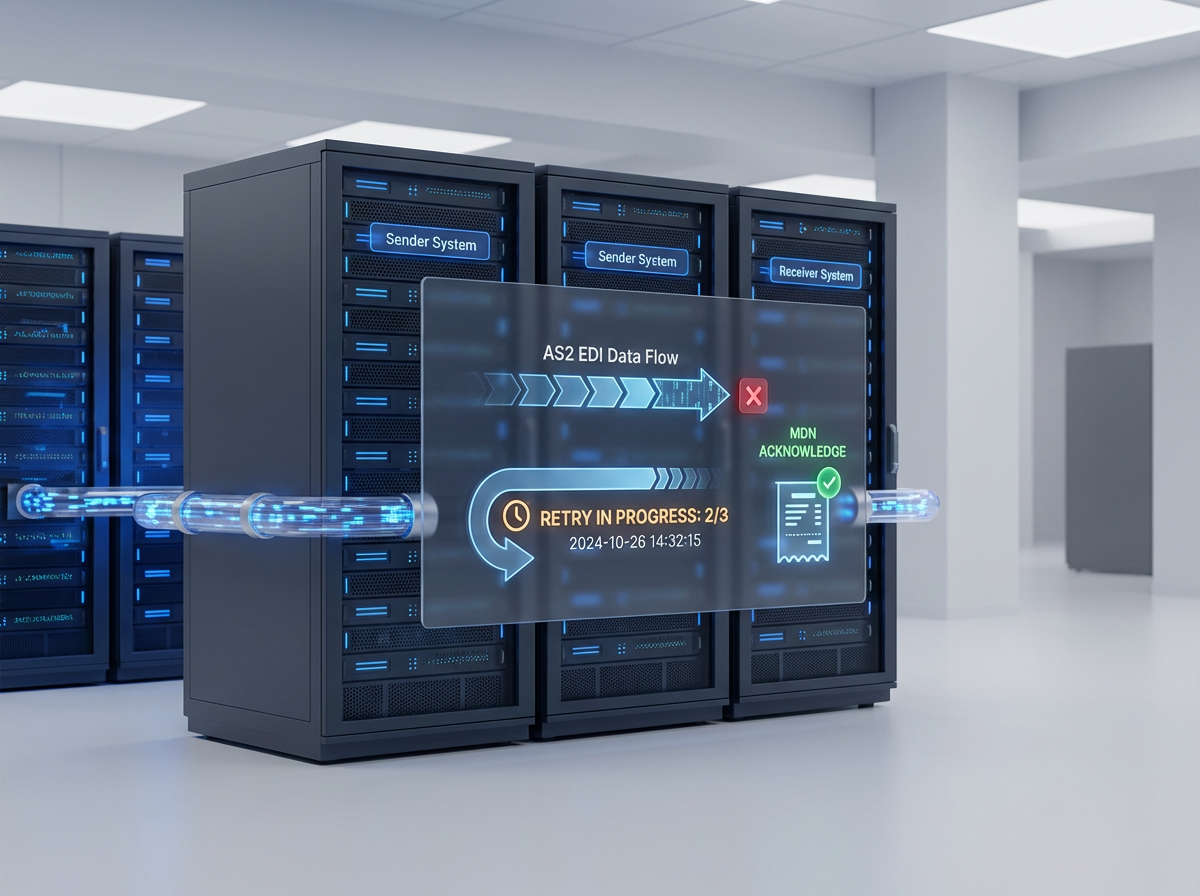
AS2: Ensuring Delivery and Integrity
Applicability Statement 2 (AS2) is a protocol designed to meet the needs of organizations requiring proof of safe delivery and data integrity. AS2 provides digital signature authentication for both senders and receivers, and supports Message Disposition Notifications (MDNs), which serve as legal proof of successful delivery. This protocol is particularly useful for organizations involved in e-commerce and supply chain transactions, where regulatory compliance and verification of file integrity is crucial.
Performance Considerations
FTPS: Speed and Flexibility
For organizations primarily concerned with transfer speed and flexibility, FTPS can be a good choice. Despite its security limitations compared to SFTP, FTPS offers faster transfer speeds, making it suitable for large file transfers or places with slow internet. Its support for both implicit and explicit SSL/TLS modes provides flexibility in configuring the level of security based on specific needs.
SFTP: Security vs. Performance
Although SFTP doesn’t match with FTPS in terms of speed, it offers a balance between security and performance. SFTP’s single-port operation simplifies firewall configurations and reduces the risk of security vulnerabilities associated with multiple open ports. SFTP is an optimal choice for organizations that prioritize security but still require reasonable performance.
Usability and Compatibility
HTTPS: Accessibility and User-Friendliness
HTTPS stands out for its ease of use and broad compatibility. By leveraging web browsers as the client interface, HTTPS eliminates the need for specialized software, making it accessible to a wide range of users. This is particularly beneficial in scenarios where non-technical users need to transfer files securely. However, organizations should carefully evaluate the security controls and data management practices of their chosen HTTPS-based service providers.
SFTP and FTPS: Wide Adoption and Interoperability
Both SFTP and FTPS are widely used and work with many different software. This means they’re good for businesses with different systems and partners. Organizations can pick the one that fits their security needs and how fast they need to transfer files.
Conclusion
Choosing the best file transfer protocol for your organization means considering security, rules you need to follow, how fast you need it, and how easy it is to use. While legacy FTP remains in use, modern alternatives like SFTP, FTPS, and HTTPS offer enhanced security and functionality, making them ideal FTP protocols for businesses. If you need extra security, AS2 is a good choice, especially for following strict rules. Evaluate your organization’s needs to choose the most suitable FTP protocol for secure and efficient file transfers.
Looking for secure file transfer options like AS2 and SFTP? Check out our product, MFT Gateway!

Talk to an EDI Expert
Join hundreds of organizations already taking full control of their B2B AS2 communications with our trusted solutions. Contact us today to tailor a solution that fits your specific AS2 EDI needs.
Related Articles
View All BlogsExplore our product stack
Try before you buy with a 30-day Free Trial
No commitment, all value. Try the AS2 Solution Risk-Free and discover how our solutions can transform your business workflows. No credit card required.
Explore Your Possibilities
Elevate AS2 Communications with our EDI and AS2 Solutions
See how our AS2 and EDI solutions can simplify your integrations, boost efficiency, and keep you compliant—request a personalized demo today.