MFT Gateway is a hosted Software as a Service (SaaS) solution that enables file exchange over the AS2 or SFTP protocol, without the need to install or maintain.
- Blog
- AS2 Message Formats: Structure, Elements & EDI Guide
EDI
AS2 Message Formats: Structure, Elements & EDI Guide
Learn the structure and key components of AS2 message formats for secure EDI data exchange. Explore X12, EDIFACT, and XML formats in this comprehensive guide.

Rusiri Samarakoon
Published: 23 Apr 2025

In the world of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), secure and effective transfer of business documents is the key. One of the most widely used protocols for this is AS2 (Applicability Statement 2). AS2 not only provides secure data transfer but also ensures message delivery in a trustworthy manner. In this article, let’s talk about AS2 message formats, their structure, elements, and implications in the world of EDI.
What is AS2?
AS2 is a protocol through which companies can send and receive EDI messages over the web in a secure manner. AS2 utilizes digital signatures and encryption to ensure privacy as well as the integrity of data being transmitted. AS2 finds vast acceptance among trading partners in manufacturing, retail, and logistics too. That’s because, with AS2, huge volumes of transactions can be easily handled effectively.
The Structure of AS2 Messages
AS2 messages consist of several key elements which work together to provide secure and trustworthy data exchange. It is important for anyone with a stake in EDI transactions to know these components.
1. Header
The AS2 message header contains essential metadata about the message, including:
- From: The identifier of the sender (usually an email address or a unique string snippet).
- To: The identifier of the recipient.
- Message-ID: A unique identifier for the message, which helps in tracking and referencing.
- Subject: A brief description of the message content.
- Date: The timestamp shows when the sender sent the message.
2. Payload
The payload is the core of the AS2 message, the actual business document being transmitted. It may be an invoice, purchase order, shipping notice, or other EDI document. The payload tends to be formatted in some universal standard, e.g., XML, EDIFACT, or X12, depending on what the trading parties require.
3. Encryption and Digital Signatures
To ensure the security of the transmitted data, AS2 messages can be encrypted and digitally signed.
- Encryption: This process transforms the payload into a format that can only be read by the intended recipient. AS2 supports various encryption algorithms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and DES (Data Encryption Standard).
- Digital Signatures: A digital signature is a cryptographic technique that verifies the authenticity of the sender. It ensures that the message has not been altered during transmission. AS2 uses public key infrastructure (PKI) to manage digital certificates for signing and verifying messages.
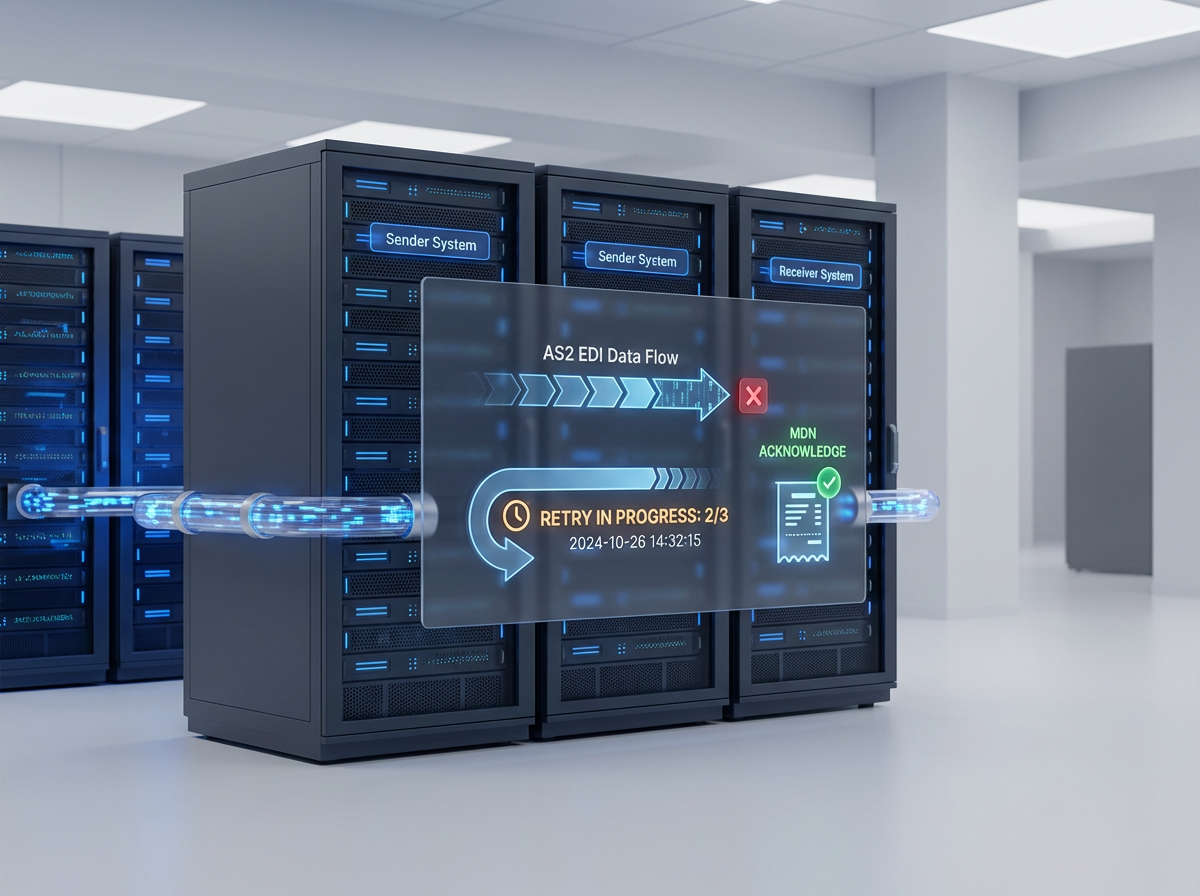
4. MDN (Message Disposition Notification)
One of the key aspects of AS2 is that it can send a Message Disposition Notification (MDN) to the sender. The MDN is similar to a receipt, which confirms that the message has been received successfully. It also indicates whether the message was processed successfully or not, and any errors that were encountered. This feedback mechanism is necessary to give assurance and accountability in EDI transactions.
AS2 Message Formats
AS2 messages can be formatted in various ways, depending on the specific requirements of the trading partners. Here are some common formats:
1. X12 Format
The X12 format is widely utilized in North America, particularly in industries such as healthcare and retail. It is a collection of elements and segments defining the structure of the document. For example, an X12 invoice can have segments representing the invoice number, date, line items, and grand total.
2. EDIFACT Format
EDIFACT (Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport) is an international standard for EDI messages. It is commonly used in Europe and other regions. EDIFACT messages are structured similarly to X12 but use different segment identifiers and formats.
3. XML Format
XML (eXtensible Markup Language) is becoming increasingly popular for EDI transactions due to its flexibility and readability. XML-based AS2 messages can be easily integrated with web services and other modern technologies, making them suitable for businesses looking to adopt a more digital approach to EDI.

Simplify your AS2 connections and make B2B communication faster, safer, and easier than ever.
Conclusion
Understanding AS2 message formats is crucial for businesses that wish to employ EDI in secure and efficient data exchange. Understanding the composition and structure of AS2 messages will allow businesses to ensure their transactions are both secure and meet industry standards. With the need for smooth communication on the rise, mastery of AS2 will be a valuable resource for businesses wishing to improve their supply chain activities and build more robust relationships with trading partners.
Looking to implement AS2 solutions for your business? Our AS2 solutions, along with our EDI Generator, can help you seamlessly integrate secure and efficient data exchange into your operations. Contact us today to learn more about our AS2 and EDI solutions.

Talk to an EDI Expert
Join hundreds of organizations already taking full control of their B2B AS2 communications with our trusted solutions. Contact us today to tailor a solution that fits your specific AS2 EDI needs.
Related Articles
View All BlogsExplore our product stack
Try before you buy with a 30-day Free Trial
No commitment, all value. Try the AS2 Solution Risk-Free and discover how our solutions can transform your business workflows. No credit card required.
Explore Your Possibilities
Elevate AS2 Communications with our EDI and AS2 Solutions
See how our AS2 and EDI solutions can simplify your integrations, boost efficiency, and keep you compliant—request a personalized demo today.